What Can Cause Pneumonia?
What Can Cause Pneumonia? Pneumonia is typically caused by infections, but various factors like bacteria, viruses, and fungi can play a role. In some cases, environmental factors and underlying health conditions can also make you more susceptible to this lung infection.
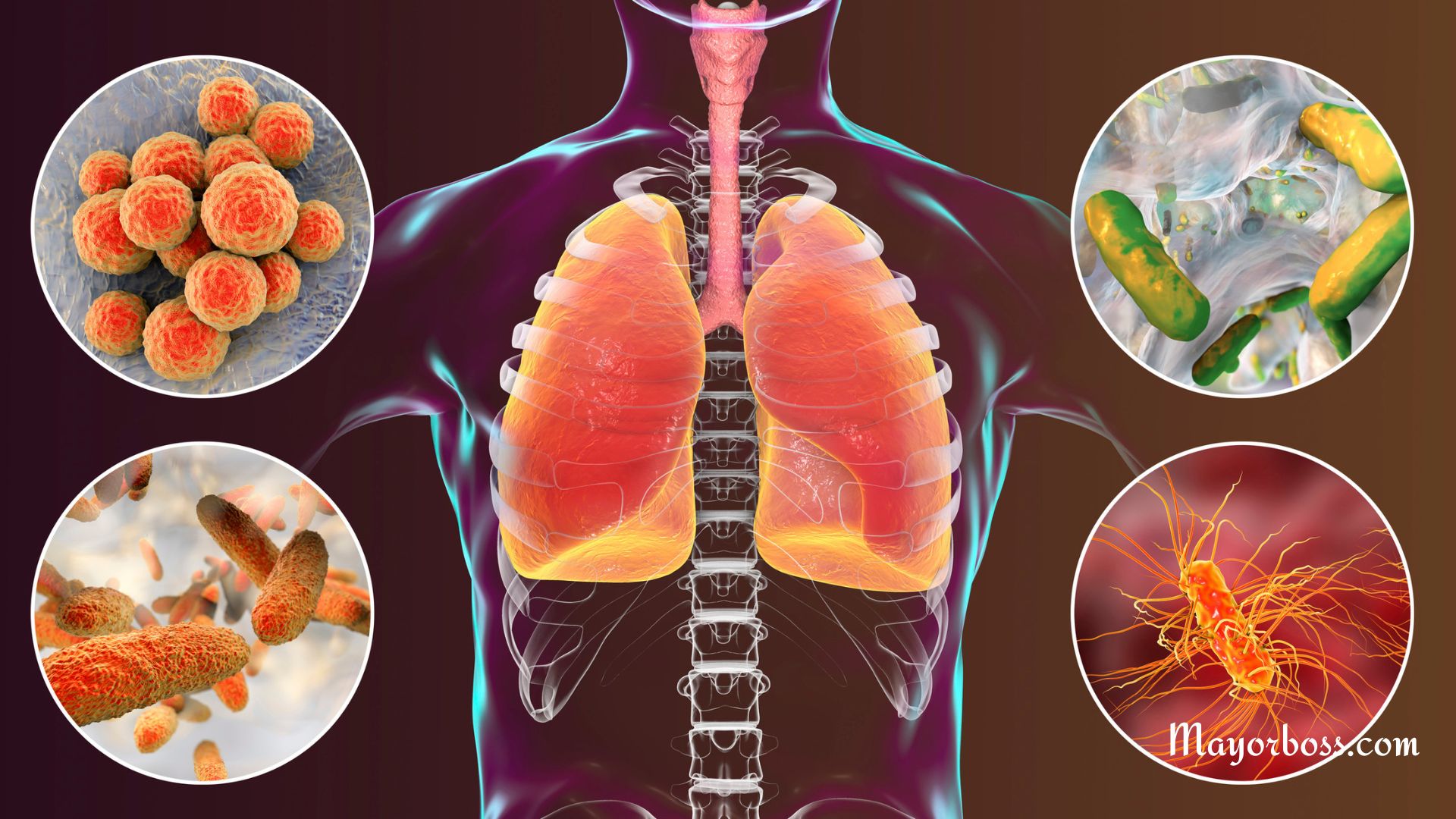
What Can Cause Pneumonia?
Bacterial Infections
The most common cause of pneumonia is bacterial infection. Streptococcus pneumoniae is often the culprit. You catch it just like you would a cold—through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing.
Viral Infections
In some cases, viruses like the flu virus or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can also cause pneumonia. Often, you’ll get a viral illness first, and then it develops into pneumonia.
Fungal Infections
In environments with a lot of bird droppings or soil, fungi like Histoplasma can cause pneumonia, particularly in people with weakened immune systems.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia
This is a less severe form of pneumonia known as “walking pneumonia.” It’s caused by Mycoplasma bacteria and usually affects younger, healthier people.
Air Pollution
Consistent exposure to poor air quality can irritate your lungs and make you more susceptible to respiratory infections, including pneumonia.
Chemical Inhalants
Inhaling chemicals, like chlorine, can also irritate the lungs and create conditions ripe for pneumonia to develop.
Chronic Illnesses
If you have a chronic illness like diabetes or heart disease, you are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Weak Immune System
People undergoing chemotherapy or those with conditions like HIV/AIDS have weakened immune systems, making it easier for pneumonia to take hold.
Age
Both the very young and the elderly are more susceptible to pneumonia due to their weaker immune systems.
Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
If you’re already in the hospital for something else, you’re at a greater risk of getting pneumonia, especially if you’re on a ventilator.
Healthcare-Associated Pneumonia
This can happen in other healthcare settings, like nursing homes or dialysis centers, where germs are more prevalent.
Smoking
Smokers have lungs that are less able to fend off infection, which increases the risk of pneumonia.
Alcohol Abuse
Excessive alcohol weakens the immune system and the lung’s natural defenses, making you more prone to pneumonia.
So, there are numerous factors that can set the stage for pneumonia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Symptoms of Pneumonia?
If you’re wondering whether you might have pneumonia, look out for symptoms like a high fever, chills, and a cough that produces phlegm. You might also feel short of breath and experience chest pain when you breathe or cough. Fatigue and muscle aches are common, too. These symptoms can vary in intensity and might not all occur at the same time.
How is Pneumonia Diagnosed?
To diagnose pneumonia, your healthcare provider will likely perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. You may also need a chest X-ray to look for inflammation in your lungs. Other tests, like blood tests or sputum cultures, can help identify the type of infection you have, which can guide treatment.
Can Pneumonia Be Prevented?
Absolutely, there are ways to lower your risk of getting pneumonia. Frequent hand-washing can help avoid infections. Vaccines for pneumonia, as well as for the flu, which can lead to pneumonia, are also available. Living a healthy lifestyle by not smoking and keeping your immune system strong through exercise and a balanced diet can also be protective.
What’s the Treatment for Pneumonia?
Treatment for pneumonia primarily depends on the cause. If bacteria are to blame, antibiotics are usually prescribed. Viral pneumonia may not respond to antibiotics and might require antiviral medication instead. For severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide respiratory support and constant monitoring.
Can Pneumonia Lead to Other Health Complications?
Yes, pneumonia can be serious and lead to complications if not treated promptly. You could develop respiratory failure, sepsis, or even lung abscesses. Additionally, pneumonia can cause lasting damage to the lung tissue, which could take weeks or months to heal. Therefore, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect you have pneumonia.
Further Reading: Symptoms of Pneumonia