5 Signs That Your Body May Be Retaining Water
Water retention, medically referred to as edema, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body’s tissues. This condition can be uncomfortable and may signal an underlying health issue. Recognizing the signs early can help you take the necessary steps to address the problem.
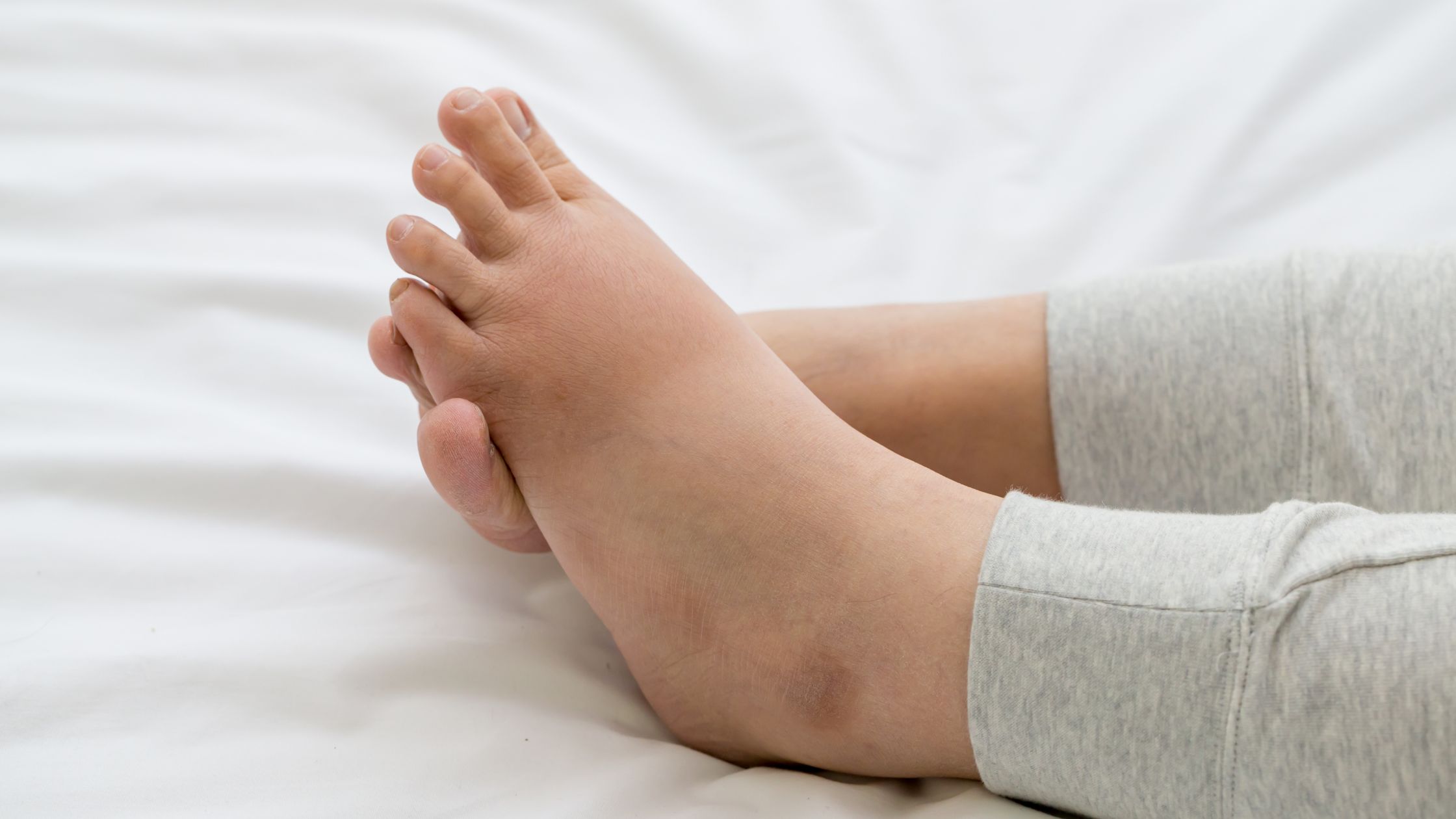
Swelling in the Legs, Ankles, and Feet May Indicate Fluid Retention
One of the most noticeable signs of water retention is swelling, particularly in the lower extremities. This happens because gravity pulls excess fluid downwards, leading to puffiness in the legs, ankles, and feet. The swelling may worsen after prolonged standing or sitting and can sometimes leave an indentation if pressed.
Unexplained Weight Gain
Sudden weight gain without changes in diet or exercise could indicate that your body is holding onto excess fluid. This type of weight gain typically occurs over a short period and may fluctuate daily. If you notice consistent increases on the scale, it may be time to consult a physician to rule out water retention.
Puffiness Around the Eyes and Face
Many people experience puffiness around the eyes and face, particularly in the morning. This can occur due to fluid shifting to these areas while lying down during sleep. Persistent puffiness might suggest that your body is struggling to regulate fluid balance effectively.
Stiffness and Joint Discomfort
Water retention can lead to joint stiffness and discomfort, making it difficult to move freely. When fluid accumulates in and around the joints, it can create a sensation of tightness and decreased flexibility, which can interfere with daily activities.
Skin Indentations and Stretching
If your skin appears stretched or leaves an indentation when pressed, it may indicate fluid retention. This condition, known as “pitting edema,” suggests that excess fluid is accumulating beneath the skin’s surface. If left untreated, it can cause discomfort and further complications.
Causes of Water Retention Vary From Lifestyle to Medical Conditions
Several aspects can contribute to fluid retention, including:
- Dietary habits: High sodium intake can cause the body to hold onto water.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of movement can lead to fluid pooling in the lower extremities.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause may contribute to water retention.
- Underlying medical conditions: Heart disease, kidney problems, and liver disorders can all impact fluid balance.
- Certain medications: Some drugs, such as corticosteroids and blood pressure medicines, can lead to fluid retention as a side effect.
Managing Water Retention Through Simple Lifestyle Changes
If you suspect that you are retaining water, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Reduce salt intake: Opt for low-sodium foods to prevent excess fluid retention.
- Stay active: Regular physical activity can help promote healthy circulation.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water can support kidney function and reduce fluid build-up.
- Elevate your legs: Raising your legs can help reduce swelling in the lower extremities.
- Consult a physician: If fluid retention persists, seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can drinking more water help reduce water retention? Yes, staying hydrated helps your kidneys function properly and can actually reduce water retention by preventing dehydration-induced fluid retention.
2. Are there any natural remedies for water retention? Some natural remedies include reducing salt intake, increasing potassium-rich foods, staying active, and consuming herbal teas such as dandelion tea, though scientific evidence is limited.
3. When should I see a doctor for water retention? You should see a doctor if the swelling is persistent, painful, or accompanied by other symptoms, such as shortness of breath or chest pain, as it could indicate a more serious underlying condition.






