Don’t Ignore Your Heartburn: 8 Causes That Need Attention
Heartburn is a common but uncomfortable experience that affects millions of people. It’s that burning sensation you feel in your chest, sometimes extending to your throat or accompanied by a sour taste in your mouth. While occasional heartburn might be easily dismissed, frequent or severe episodes shouldn’t be taken lightly. Comprehending potential heartburn causes is pivotal to finding relief and protecting your esophagus.

What is Heartburn?
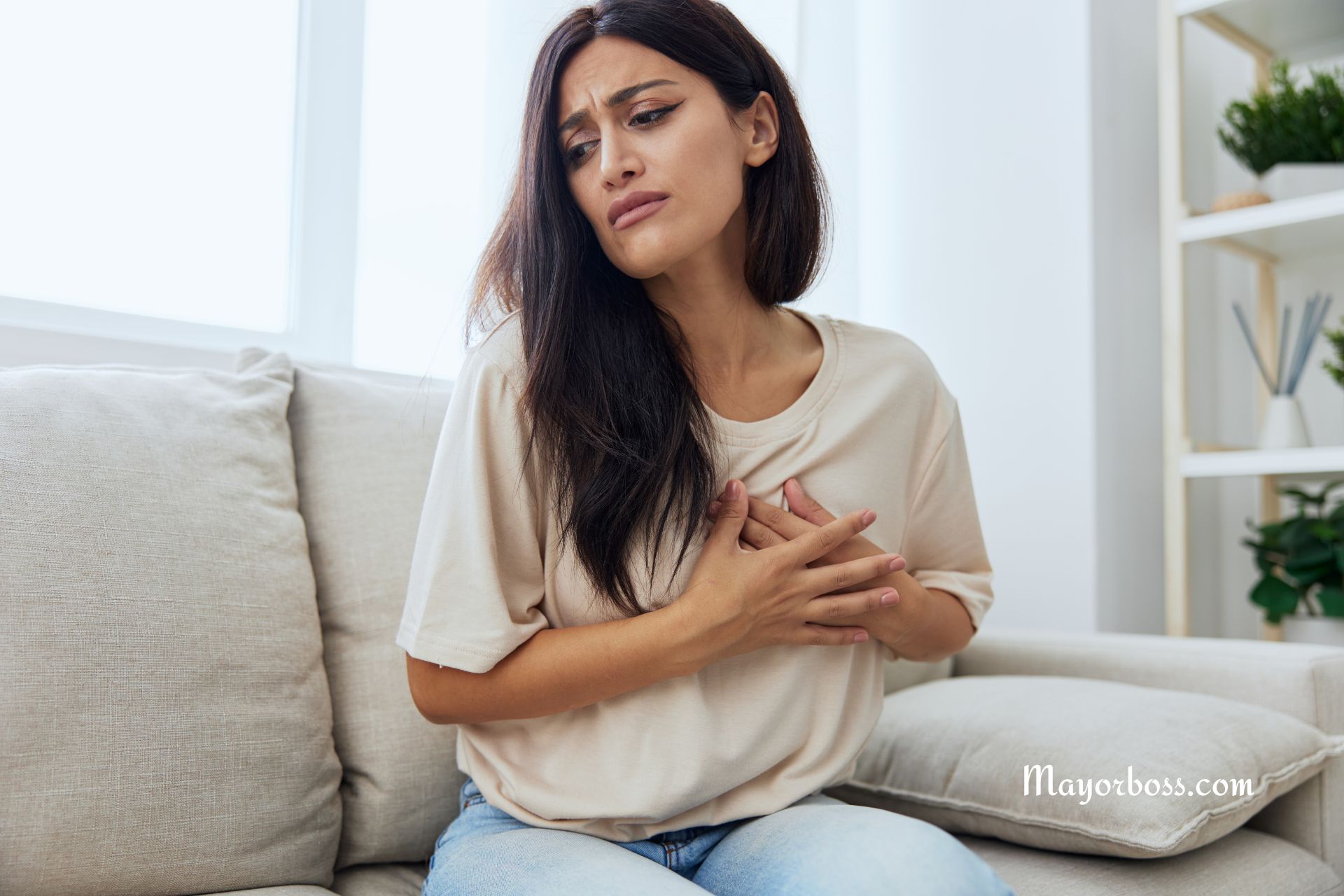
Heartburn is a burning sensation that typically occurs in the chest, just behind the breastbone. It usually happens after eating and might get worse when you bend over or lie down. Although heartburn is common, experiencing it frequently might point to a need for a closer look at your health.
Common Heartburn Causes
Here are eight common causes of heartburn that might need your attention:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): The most frequent cause of chronic heartburn, GERD happens when the muscle at the bottom of your esophagus (lower esophageal sphincter) weakens. This allows stomach content to come back up, irritating the lining of your esophagus.
- Diet: Certain foods trigger heartburn for many people. Common culprits include:
- Fatty or fried foods
- Spicy foods
- Citrus fruits
- Tomatoes and tomato products
- Chocolate
- Peppermint
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Hiatal Hernia: It occurs when part of your stomach pushes above your diaphragm (the muscle separating your chest and abdomen). This disrupts the normal barrier against reflux.
- Overeating: Eating large meals puts pressure on your stomach, increasing the risk of backflow into the esophagus.
- Eating Close to Bedtime: Lying down soon after a meal slows digestion and makes acid reflux more likely.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and the growing baby’s pressure on the stomach can trigger heartburn, especially in later pregnancy.
- Medications: Certain medications, including some blood pressure medicines, antidepressants, and pain relievers, can relax the lower esophageal sphincter or irritate the esophagus.
- Smoking: smoking can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, leading to heartburn. Additionally, smoking can decrease saliva production, which helps neutralize acid in the esophagus.
When to Worry About Heartburn
While occasional heartburn is often manageable at home, sometimes it can signal a more serious condition. Seek medical advice if you experience:
- Heartburn that occurs more than twice a week
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain, especially if it’s accompanied by shortness of breath or jaw pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Weight loss without trying
- Black or bloody stools
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I relieve heartburn naturally? A: Several lifestyle changes can help:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid trigger foods.
- Eat smaller meals.
- Don’t lie down right after eating.
- Elevate the head of your bed.
- Quit smoking.
Q: Are there over-the-counter medications for heartburn? A: Yes, options include:
- Antacids (for quick but short-term relief)
- H2 blockers (reduce acid production for some hours)
- Proton pump inhibitors (block acid production for longer periods)
Q: When should I see a doctor about my heartburn? A: Aside from the red-flag symptoms mentioned above, consult your doctor if self-care and over-the-counter treatments fail to control your heartburn, or you need them frequently.
Summary
Heartburn is a common issue caused by stomach acid backing up into the esophagus. Frequent or severe heartburn can indicate an underlying condition such as GERD. It’s important to identify and address potential causes for long-term relief. If you’re experiencing frequent or severe heartburn or “red flag” symptoms, consult your doctor to rule out underlying conditions and develop an appropriate treatment plan.