Hormonal Imbalance in Women
Hormonal imbalance in women is a common yet often misunderstood health issue. This article aims to shed light on this prevalent condition, providing insights into its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.
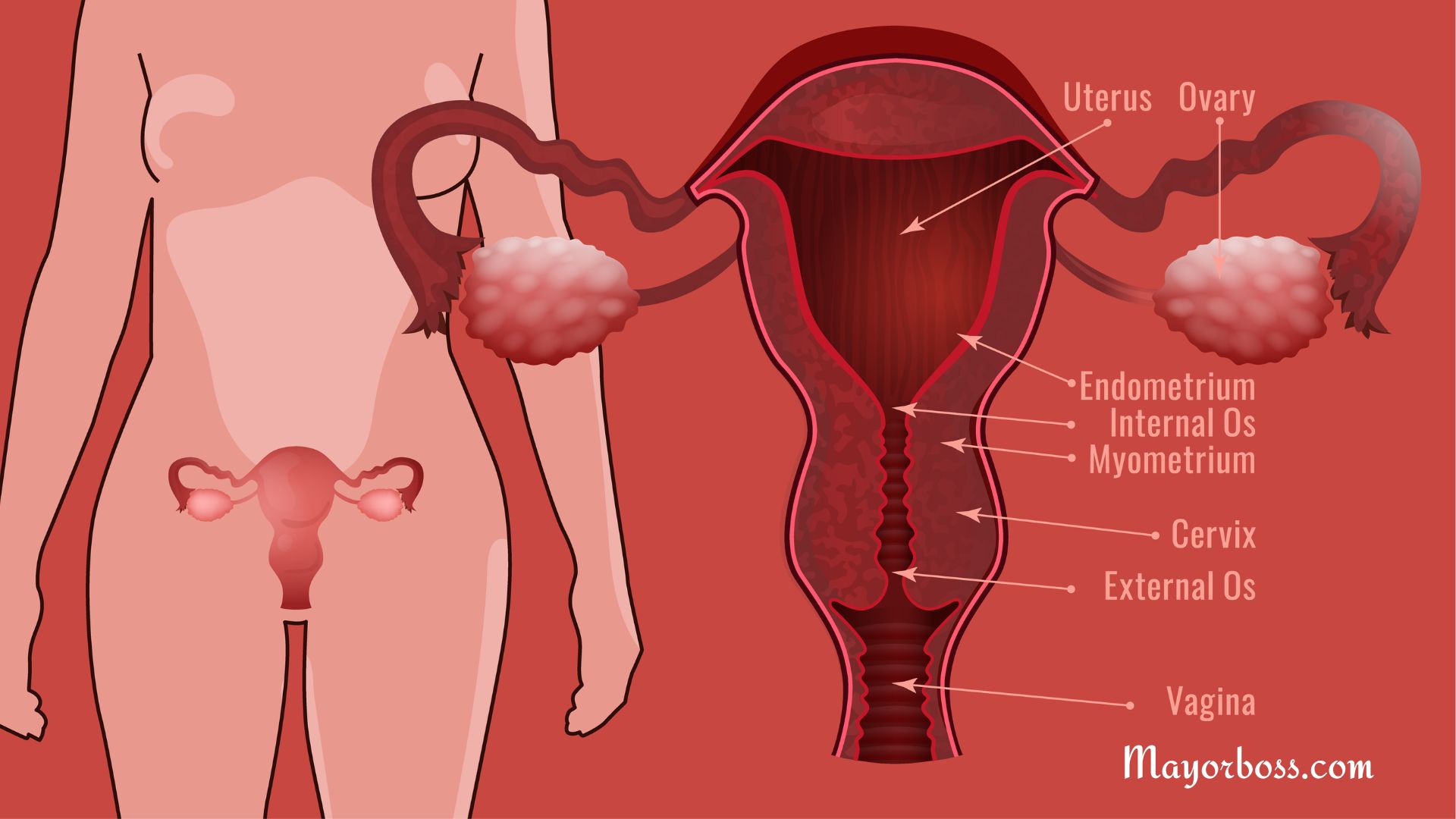
What is a hormonal imbalance?
Hormonal imbalance generally happens when there is too much or too little of a particular hormone in your bloodstream. Because hormones play a crucial role in regulating major bodily functions, even the smallest imbalance can cause significant side effects. In women, hormonal imbalances often become apparent around times of major life changes, such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
What are the signs of hormonal imbalance in a woman?

The signs of a hormone imbalance can vary depending on which hormone is out of balance. However, common signs and symptoms associated with a hormone imbalance in women include:
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Sleep problems
- Mood changes
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Headaches
- Depression
- Memory problems
- Changes in appetite
- Low sex drive
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Vaginal dryness
- Pain during sex
- Increased or decreased heart rate
- Weight gain
- Increased hunger
- Unexplained sudden weight loss
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches and pains
- Joint pain
- Dry skin
- Changes in sensitivity to heat or cold
- Infertility
- Hair loss
- Thinning hair or brittle hair
- Puffy face
- Heavy or irregular periods
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it’s important to see your doctor if you’re experiencing any of them.
What are the causes of hormonal imbalance in women?
Here’s a simple table that organizes the potential causes of hormonal imbalance in women:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Endocrine Disorders | Conditions such as PCOS, thyroid disorders, and diabetes can disrupt hormone balance. |
| Menopause | This natural transition phase can cause various hormonal changes leading to imbalances. |
| Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | The body undergoes significant hormonal changes during these times, potentially causing imbalances. |
| Hormonal Birth Control | Contraceptives like the pill, IUDs, patches, and injections can affect hormone levels. |
| Eating Disorders | Disorders like anorexia or bulimia can disrupt hormone production. |
| Chronic Stress | Long-term stress can significantly impact hormone balance, particularly cortisol levels. |
| Insufficient Sleep | Lack of sleep can affect several hormones, including cortisol, insulin, and growth hormones. |
| Poor Nutrition | A diet lacking in essential nutrients can disrupt hormone production and regulation. |
| Excessive Alcohol or Drug Use | Both can affect hormone production and function. |
| Physical Inactivity | Regular exercise is important for maintaining hormone balance. Lack of it can contribute to imbalance. |
| Exposure to Toxins, Pollutants, and Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals | These can interfere with hormone production and function. |
| Underlying Health Conditions | Other medical conditions, such as pituitary tumors or certain types of cancer, can cause hormonal imbalances. |
Diagnosing Hormonal Imbalance in Women
Diagnosing hormonal imbalances in women involves a step-by-step process to assess symptoms, take a medical history, and conduct specific tests. Here’s how it generally unfolds:
1. Initial Consultation:
Your healthcare provider will begin by discussing your symptoms and medical history. They’ll want to understand the nature of your symptoms, their duration, and any patterns you’ve noticed.
2. Physical Examination:
Next, you’ll undergo a physical examination, which allows your doctor to look for any physical signs of hormonal imbalance. These might include acne, weight gain, or hair loss.
3. Blood Tests:
The most common way to diagnose hormonal imbalances is through blood tests. These tests can measure levels of various hormones in your body. The specific hormones tested will depend on your symptoms and medical history.
4. Additional Tests:
In some cases, your doctor may order additional tests to rule out other conditions or to further investigate the cause of your hormonal imbalance. These could include imaging tests, like ultrasound or MRI, to check for problems with your endocrine glands.
5. Referral to a Specialist:
If your regular healthcare provider cannot pinpoint the cause of your hormonal imbalance, you might be referred to an endocrinologist, a doctor who specializes in hormonal issues.
Once a hormonal imbalance is diagnosed, your healthcare provider can guide you on the appropriate treatment options. This may include medication, lifestyle changes, or even surgery in some cases. It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s advice to manage hormonal imbalances effectively.
How is hormonal imbalance treated in women?
The treatment for a hormone imbalance will depend on the underlying cause. For example, if the cause is menopause, treatment may involve hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
HRT can be taken as a pill, skin patch, gel, vaginal cream, or injection. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of HRT before starting treatment.
Other possible treatments for a hormone imbalance include:
- Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise
- Stress management such as yoga, meditation, or aromatherapy
- Weight loss, if needed
- Supplements such as vitamin D or calcium
- Hormonal birth control: This can help regulate hormone levels in women of childbearing age. Common hormonal birth control options include the pill, patch, ring, shot, and intrauterine device (IUD).
- Thyroid hormone therapy: This is often the first line of treatment for an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Synthetic thyroid hormone replacement pills are taken daily to help regulate the body’s metabolism and energy levels.
- Metformin: This is a medication that is often used to treat type 2 diabetes.
- Anti-androgen medications: These are drugs that block the effects of hormones androgens and are often used to treat acne and excess hair growth.
- Spironolactone: This is a medication that is often used to treat heart failure, high blood pressure, and low potassium levels.
- Levothyroxine: This is a synthetic form of the hormone thyroxine and is used to treat an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism).
Frequently Asked Questions about Hormonal Imbalance in Women
Common signs of hormonal imbalance in women generally include irregular periods or changes in menstrual flow, unexplained weight gain or weight loss, bloating, mood swings, fatigue, changes in sleep patterns, skin rashes, and changes in libido.
Generally speaking, there are several potential causes of hormonal imbalance in women, including endocrine disorders like PCOS or thyroid conditions, lifestyle factors like poor diet and chronic stress, transitions such as menopause and pregnancy, and certain medications like hormonal birth control.
Hormonal imbalance is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specific blood tests to measure hormone levels. In some cases, additional tests like imaging studies may be used to identify issues with endocrine glands.
Treatment for hormonal imbalance in women depends on the underlying cause but can include hormone replacement therapy, medications for underlying conditions, lifestyle changes, alternative therapies, and in rare cases, surgery.
Always consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.