Lipedema: What Is It, and How Is It Treated?
Have you ever noticed that some people have a significant difference in size between their upper and lower body? Or maybe you’ve seen someone with legs that seem disproportionately larger compared to their waist and arms, even though they’re not overweight overall? This could be a condition called lipedema. It’s a term that many people haven’t heard of, yet it affects millions, mostly women. Below, you will find what lipedema is, how to recognize it, and what treatment options are available.
What Exactly Is Lipedema?
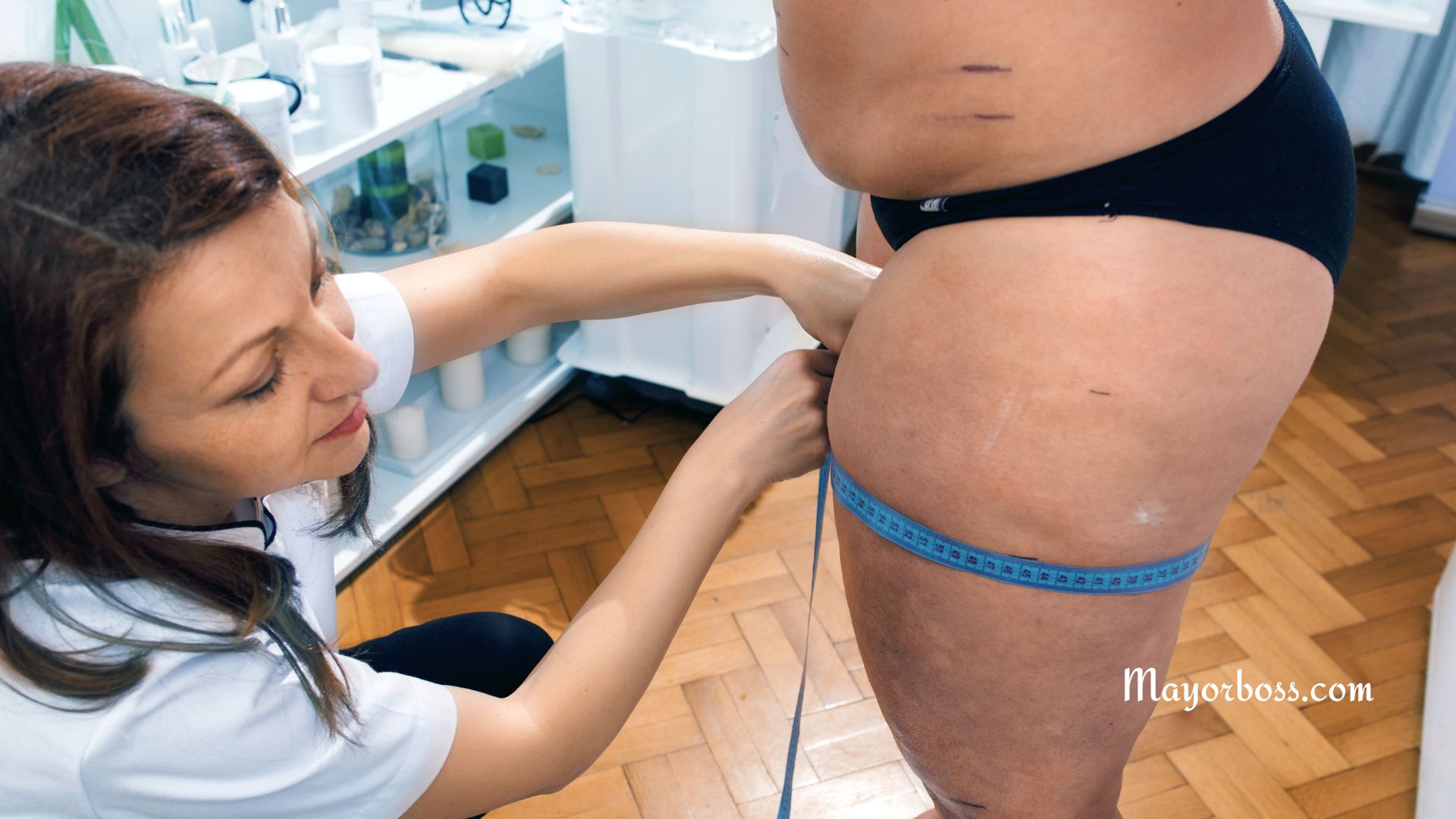
Lipedema is a common long-term condition characterized by an abnormal buildup of fat, typically in the lower half of the body. This fat accumulates disproportionately on the hips, thighs, buttocks, and sometimes the arms, but not the feet or hands. The condition usually begins or worsens during times of hormonal change, such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
Why Does Lipedema Happen?
The exact cause of lipedema isn’t fully understood, but there’s a strong genetic link. This means if your mother or grandmother had it, you might be at risk, too. Hormonal changes also play a role, which is why lipedema often appears or worsens during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
What Are the Symptoms of Lipedema?
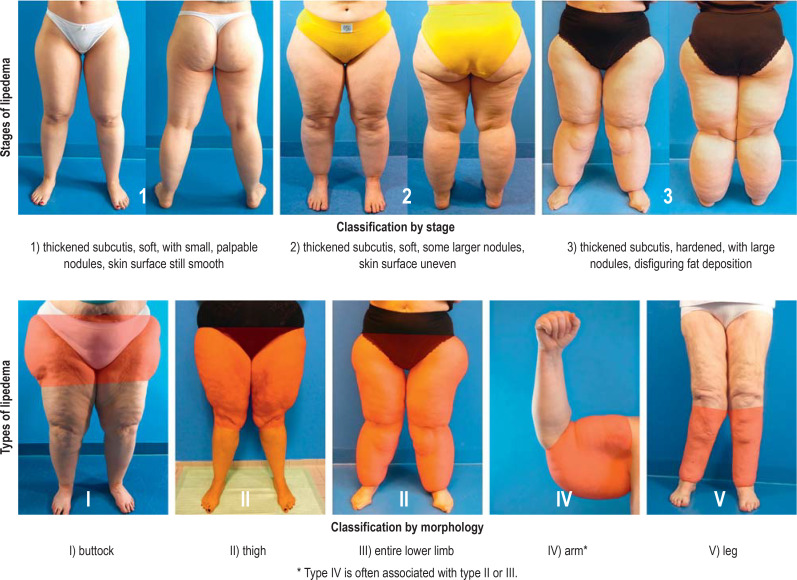
If you’re contemplating whether you or someone you know might have lipedema, here are some common signs:
You Notice Disproportionate Fat Distribution
The most noticeable symptom of lipedema is a disproportionate distribution of fat. Your lower body, including your hips, thighs, and legs, appears much larger compared to your upper body. This imbalance can make clothes shopping a real hassle.
You Feel Pain and Tenderness
Lipedema is not just about looks. The affected areas often feel painful and tender. You might experience a heavy, achy feeling in your legs, making it difficult to move around comfortably.
You Experience Easy Bruising
People with lipedema bruise easily. Even a light touch or bump can result in significant bruising, which can be both painful and embarrassing.
Swelling That Doesn’t Go Away
Unlike regular swelling, lipedema-related swelling doesn’t improve with rest or elevation. It can worsen as the day goes on, making it hard to stay active.
How Is Lipedema Diagnosed?
Diagnosing lipedema can be tricky because it’s often mistaken for regular obesity or lymphedema (a condition where lymph fluid builds up in tissues). Doctors typically diagnose lipedema based on a physical examination and the patient’s medical history. They look for the characteristic fat distribution and check for other symptoms like pain and bruising.
What Are the Treatment Options for Lipedema?
Unfortunately, there’s no cure for lipedema, but there are several ways to manage its symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Compression Therapy
One of the most common treatments is compression therapy. Wearing compression garments, like stockings or sleeves, can help reduce swelling and pain by improving lymphatic flow and providing support to the affected tissues.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
MLD is a specialized type of massage that encourages the movement of lymph fluid out of the swollen areas. This gentle massage can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Exercise
Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or walking are recommended for people with lipedema. These activities can improve circulation and help manage symptoms without putting too much stress on the joints.
Diet
While diet alone can’t cure lipedema, maintaining a healthy weight is important. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage symptoms. Some people with lipedema find that reducing salt intake and eating a low-carb, high-protein diet helps with swelling and pain.
Liposuction
In more severe cases, liposuction might be considered. Unlike traditional liposuction, specialized techniques like water-assisted or tumescent liposuction are used to remove the abnormal fat deposits. This procedure can significantly decrease pain and improve mobility.
How Can You Live with Lipedema?
Embrace Support
Living with lipedema can be emotionally challenging, both physically and emotionally. It’s important to seek support from friends, family, or support groups. Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can make a big difference.
Be Kind to Yourself
Lipedema can be tough on your self-esteem. Keep in mind your worth is not defined by your appearance. Treat yourself with kindness and focus on what makes you happy and healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Men Get Lipedema?
While lipedema predominantly affects women, men can develop it, though it is rare. Hormonal differences are a key factor in why it is more common in women.
Is Lipedema the Same as Obesity?
No, lipedema and obesity are not the same. Lipedema is a disease of the fat cells and lymphatic system, while obesity is a result of excessive caloric intake and insufficient physical activity. Lipedema fat does not respond well to typical weight loss methods.
Can Lipedema Be Prevented?
There is no known way to prevent lipedema. However, early diagnosis and management can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. If you notice signs of lipedema, consult a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment options.
Can lipedema be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for lipedema, but treatments like liposuction can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lipedema is a complex condition, but with the right knowledge and support, you can manage its symptoms and lead a fulfilling life. If you suspect you have lipedema, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice and explore the treatment options available to you.






