What Is Lung Cancer?
- Lung cancer is a type of cancer that affects the lungs.
- It is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women.
- Lung cancer can be caused by smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, asbestos, and other environmental and lifestyle factors.
- Symptoms of lung cancer may include coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and more.
- Lung cancer is treated with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and other treatments.
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest cancers in the world. In the United States, it accounts for more deaths than colorectal, breast, and prostate cancers combined, according to the American Cancer Society. (1)
Despite these alarming facts, lung cancer is often considered a “silent disease” because many people are unaware of the early warning signs.
This post will provide you with everything you need to know about lung cancer, including risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options.
Let’s get started by discussing what exactly lung cancer is.
What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are a pair of organs located in the chest that help you breathe. They are made up of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which are connected to the trachea (windpipe) by a network of small airways.
The trachea branches into the left and right bronchi, which are the two main tubes that carry air into and out of the lungs. Cancer can develop in any part of the lungs, but it most commonly starts in the bronchi. (2, 3)
Types of lung cancer
There are two main types of lung cancer—non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC makes up about 85% of all cases and is divided into several subtypes based on how the cells look under a microscope. The three most common subtypes are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. SCLC accounts for about 15% of all cases. (4,5, 6)
What are the symptoms of lung cancer?
The most common symptom of lung cancer is a cough that doesn’t go away or gets worse over time. Other symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in your chest or back that worsens with coughing or deep breathing
- Coughing up blood
- Hoarseness
- Frequent infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia
- Wheezing
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite or weight loss
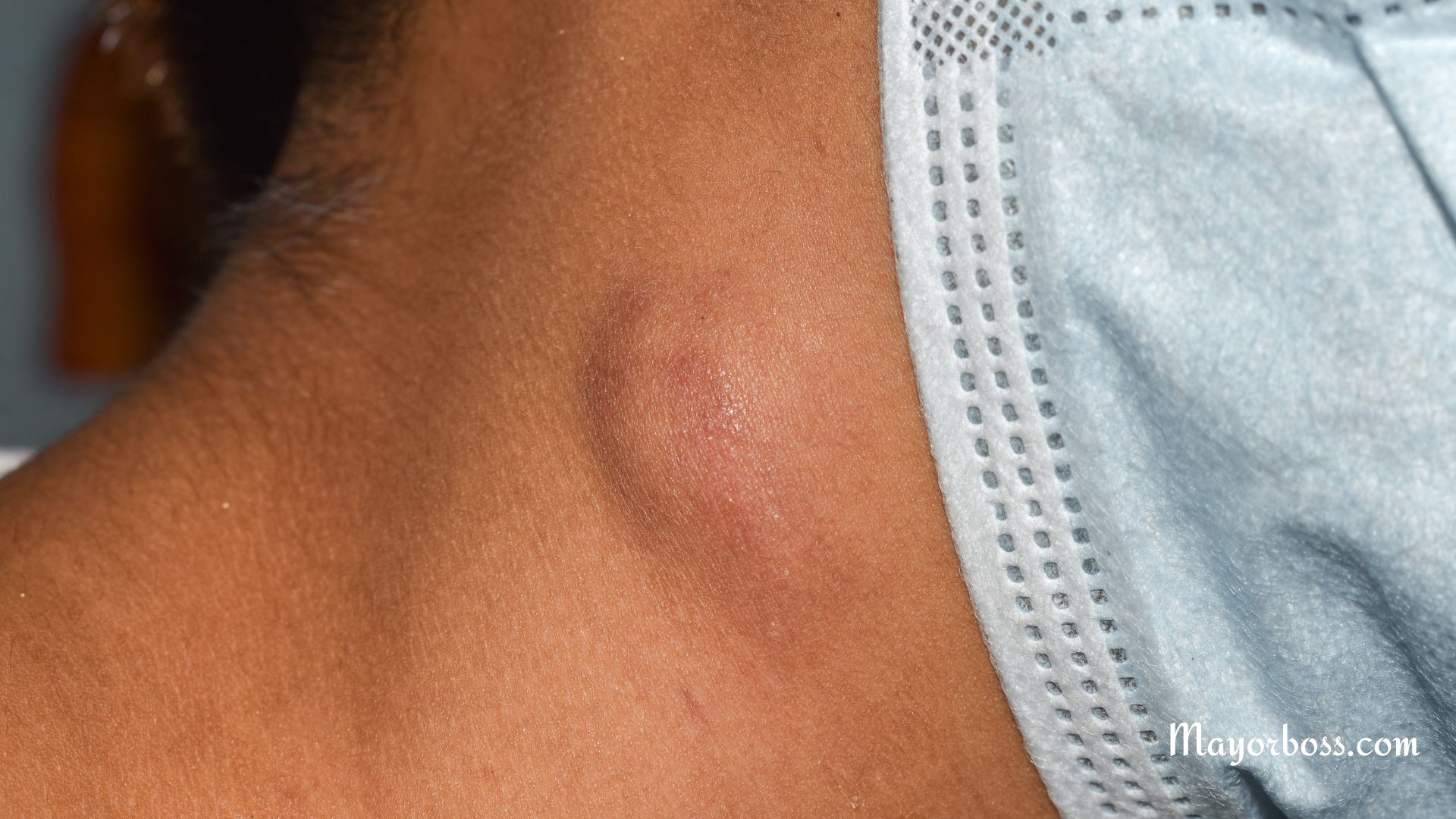
- Swelling in your neck or face
- Bone pain
- Clubbing (enlargement and rounding of the tips of the fingers).
Lung cancer symptoms often resemble those of other conditions, such as COPD, asthma, pneumonia, acid reflux, and heart disease. This can make diagnosis difficult. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your doctor. They can order tests to determine whether you have lung cancer or another condition. (7, 8, 9, 10)
Risk Factors
There are many factors that can increase your risk of developing lung cancer. The most significant risk factor is smoking tobacco. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 80% of lung cancer deaths in the United States are caused by smoking. (11)
Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution. People with a history of lung diseases, such as COPD and tuberculosis, are also at an increased risk. Certain genetic conditions, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and familial non-polyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome), can also increase your risk. (12, 13)
Lung Cancer Screening
Screening for lung cancer is recommended for people who are at high risk. This includes people who are current or former smokers aged 55 to 74. Screening is typically done with a low-dose CT scan. This is a type of X-ray that can detect lung cancer at an early stage when it is most treatable.
Treatment
The treatment of lung cancer depends on the type, stage, and location of the disease. It may also depend on your overall health and preferences. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
- Surgery is the most common treatment for early-stage lung cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous tumor and any surrounding tissue.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy uses drugs that target specific mutations in cancer cells. (14, 15, 16)
Side effects of lung cancer treatment
The side effects of lung cancer treatment can vary depending on the type and intensity of the treatment. Common side effects of lung cancer treatment include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Long-term lung cancer treatments can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart problems, lung damage, joint pain, nerve problems, and digestion problems. (17)
Before starting treatment, be sure to talk to your doctor about the potential side effects.
Prevention
There is no sure way to prevent lung cancer. However, quitting smoking is the best way to reduce your risk. If you don’t smoke, avoid exposure to secondhand smoke. You should also avoid exposure to radon, asbestos, and cancer-causing chemicals.
In particular, eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and get vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia. These measures can help keep your lungs healthy and reduce your risk of lung cancer. (18, 19)
Takeaway
Lung cancer is a serious disease with few symptoms in its early stages. However, there are treatments available if the cancer is caught early. The best way to prevent lung cancer is to quit smoking. If you are a smoker, talk to your doctor about ways to quit.
If you are at high risk for lung cancer, talk to your doctor about whether you should be screened for the disease.