What Is Atherosclerosis?
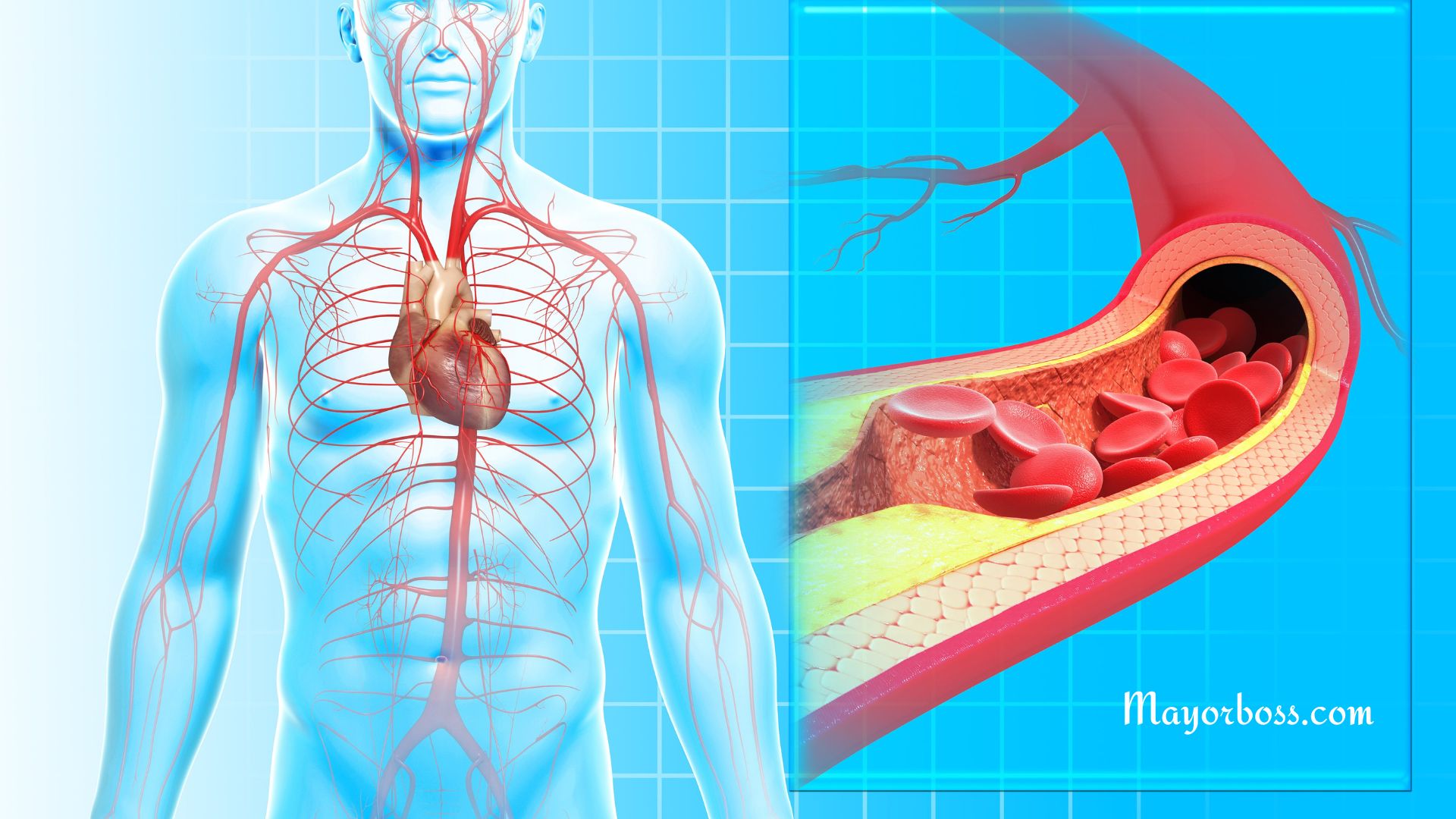
What Is Atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis is a condition where fatty deposits accumulate on the walls of your arteries, narrowing them over time. This can limit blood flow and lead to serious health problems, such as heart attack, stroke, or even death.
What Exactly Happens in Atherosclerosis?
In atherosclerosis, plaque—a mix of fat, cholesterol, and other substances—starts to build up on the inner walls of your arteries. Initially, this might not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as the plaque increases, it narrows the arteries and limits blood flow. In severe cases, a piece of the plaque can break off, causing a blood clot and potentially leading to a heart attack or stroke.
What Causes Atherosclerosis?
Various factors can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood play a significant role. Additionally, lifestyle choices like poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking are common culprits. High blood pressure and diabetes can also speed up the process. In people with a family history of heart disease, the risk tends to be higher.
What Are the Symptoms?
Often, atherosclerosis doesn’t show any symptoms until it’s fairly advanced. When symptoms do appear, they can vary based on which arteries are affected. For instance, blocked arteries in your heart may cause chest pain, while in your legs, you might experience muscle pain or numbness.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Doctors usually start with a physical exam and questions about your medical history. Then, they may recommend tests like blood tests, ultrasound, or angiography to visualize the arteries. Many scientists believe early detection through regular check-ups is crucial for effective management.
How Can You Prevent Atherosclerosis?
Prevention is key, and it’s never too early to start taking steps to protect your arteries. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can go a long way. Regular exercise, even just 30 minutes a day, can also make a significant impact. Quitting smoking and controlling existing health conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes are other effective ways to reduce your risk.
What Are the Treatment Options?
Treatment often involves lifestyle changes and medication. Examples of medications used are statins to lower cholesterol, antihypertensive drugs for high blood pressure, and antiplatelet agents to prevent blood clots. In severe cases, surgical procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery might be necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Exactly Is Plaque and How Does It Form in Arteries?
Plaque is a sticky substance made up of various elements like fat, cholesterol, and calcium. It begins to accumulate on the walls of your arteries, usually starting in small amounts. Over time, this plaque hardens and narrows the arterial passage, restricting blood flow. The formation of plaque is often influenced by high cholesterol levels, poor lifestyle choices, and other health conditions such as diabetes.
How Do I Know If I’m at Risk for Developing Atherosclerosis?
Several factors can put you at higher risk for developing this condition. These include age, high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, high blood pressure, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and lack of exercise. If you have a family history of heart disease or other cardiovascular issues, your risk increases further. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help assess your risk level and guide preventive measures.
How Can Atherosclerosis Lead to a Heart Attack or Stroke?
When plaque builds up in the coronary arteries that supply blood to your heart, it limits the blood flow. If a piece of plaque breaks free, it can create a blood clot. This clot can block the artery entirely, cutting off blood supply to a portion of the heart or brain, thereby causing a heart attack or stroke.
Are There Any Early Warning Signs of Atherosclerosis?
In many cases, atherosclerosis develops gradually and doesn’t show symptoms until an artery is significantly blocked. However, when symptoms do appear, they can vary depending on which arteries are affected. For example, atherosclerosis in the heart arteries may result in chest pain or discomfort, while blockages in the arteries supplying the legs can cause leg pain, numbness, or weakness. Therefore, regular medical check-ups are vital for early detection and management.
Are There Specific Tests for Diagnosing Atherosclerosis?
Yes, there are various diagnostic methods to confirm atherosclerosis. Blood tests can help assess cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Imaging tests like ultrasounds or angiograms provide a visual representation of the state of your arteries. These tests are critical for early detection and effective management of the condition.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help in Preventing Atherosclerosis?
Adopting a healthier lifestyle is crucial in preventing atherosclerosis. Eating a balanced diet that is low in saturated fats and high in fiber can help manage cholesterol levels. Exercise is another important factor; even moderate physical activity can improve your heart health. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake are additional ways to lower your risk.
What Are the Possible Side Effects of Medications Used for Treating Atherosclerosis?
Medications like statins, which are commonly used to lower cholesterol, can have side effects such as muscle pain, liver damage, or digestive problems. Antihypertensive drugs may cause dizziness, headaches, or even kidney issues in some cases. Always consult your healthcare provider for a medication plan that suits your needs and monitor for any adverse reactions.
Can Atherosclerosis Be Reversed?
Unfortunately, once plaque builds up in the arteries, it’s challenging to completely reverse atherosclerosis. However, lifestyle changes and medication can stabilize or slow down the progression of the disease. In some instances, treatments like angioplasty and stent placement can open up narrowed arteries and improve blood flow. But the most effective strategy is prevention, which includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and other lifestyle changes.
What’s the Difference Between Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis?
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis refers to the general hardening and thickening of the arterial walls, which can happen for various reasons. Atherosclerosis is specifically the buildup of plaque on the artery walls. Both conditions can impair blood flow, but atherosclerosis is more likely to result in severe cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks or strokes.