What is Caffeine?
In simple words, caffeine is a naturally occurring stimulant most commonly found in coffee, tea, cola, and cacao plants. It’s also present in various foods, beverages, and medications. When you consume caffeine, it works by stimulating your central nervous system, which can help keep you awake and reduce the feeling of being tired. In fact, it is one of the most widely used drugs in the globe.
How Caffeine Affects Your Body

Boosting Alertness
Caffeine is well-known for its ability to increase alertness. It does this by blocking a neurotransmitter in your brain called adenosine, which typically promotes sleep and relaxation. Consequently, caffeine keeps you more alert and awake.
Other Effects on the Body
Aside from keeping you alert, caffeine can also increase your heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. For some people, it enhances physical performance and increases metabolism, which is why it’s often included in weight loss supplements.
Mood and Brain Function
Caffeine can also affect your mood and brain function. It’s known to improve concentration, and for some, it can enhance short-term memory. However, reactions to caffeine can vary widely among individuals.
Sources of Caffeine
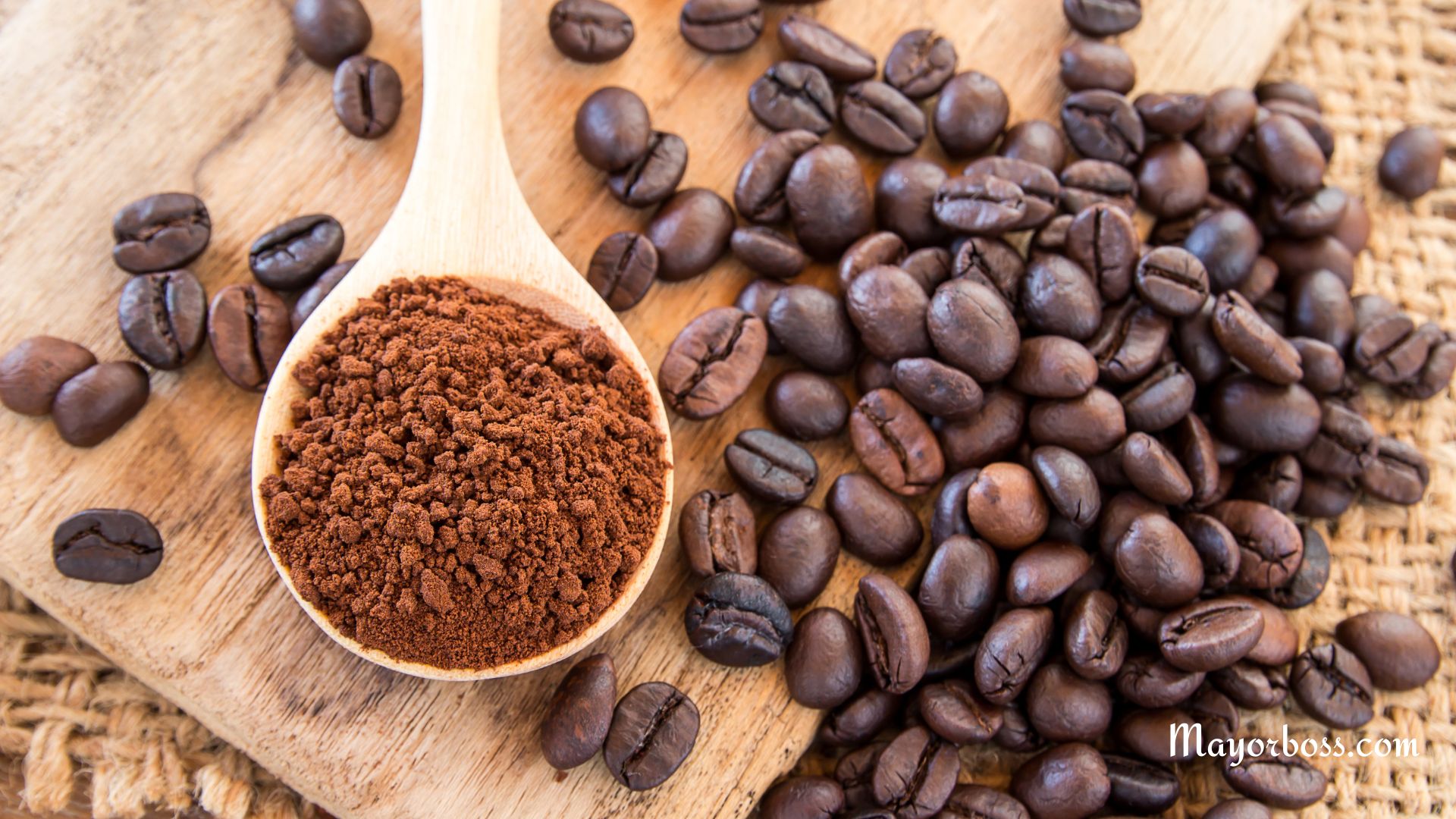
Coffee and Tea
The most common sources of caffeine are coffee and tea. The amount of caffeine in these drinks can vary greatly depending on the type of coffee or tea and how it’s prepared.
Chocolate and Soft Drinks
Caffeine is also found in chocolate, particularly dark chocolate, and many soft drinks, like cola.
Medications and Supplements
Some over-the-counter and prescription medications contain caffeine, often for its pain-relieving properties. Additionally, energy drinks and workout supplements frequently include caffeine for its stimulant effects.
Caffeine Sensitivity
Individual Variations
People’s sensitivity to caffeine varies. Some might feel jittery or anxious after just a small amount, while others can consume much more without noticeable effects.
Factors Influencing Sensitivity
Factors influencing this sensitivity include genetics, age, body weight, and tolerance developed over time.
Potential Drawbacks
Sleep Disruption
One of the most common side effects of caffeine is disrupted sleep. Consuming caffeine late in the day can typically interfere with your sleep cycle, leading to insomnia or reduced sleep quality.
Dependence and Withdrawal
Regular caffeine use can lead to dependence. If you suddenly stop consuming caffeine, you might experience withdrawal symptoms like decreased energy, headaches, depressed mood, fatigue, drowsiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Other Negative Effects
In some people, too much caffeine can lead to increased heart rate, anxiety, digestive issues, and potentially increased blood pressure.
Conclusion
Caffeine, widely consumed around the world, is a powerful stimulant with a range of effects on the body. While it can boost alertness and enhance certain physical and mental functions, it’s important to be aware of your individual sensitivity and potential negative effects, especially regarding sleep and dependence. Moderation is key to enjoying the advantages of caffeine without experiencing the downsides.