6 Things That Happen to Your Body When You’re Angry
Anger, one of the most intense human emotions, can have a significant impact on your body. It’s not just an emotional state; it physically alters your body in ways you may not even realize. In this article, I’ll detail six surprising things that happen to your body when you’re angry.
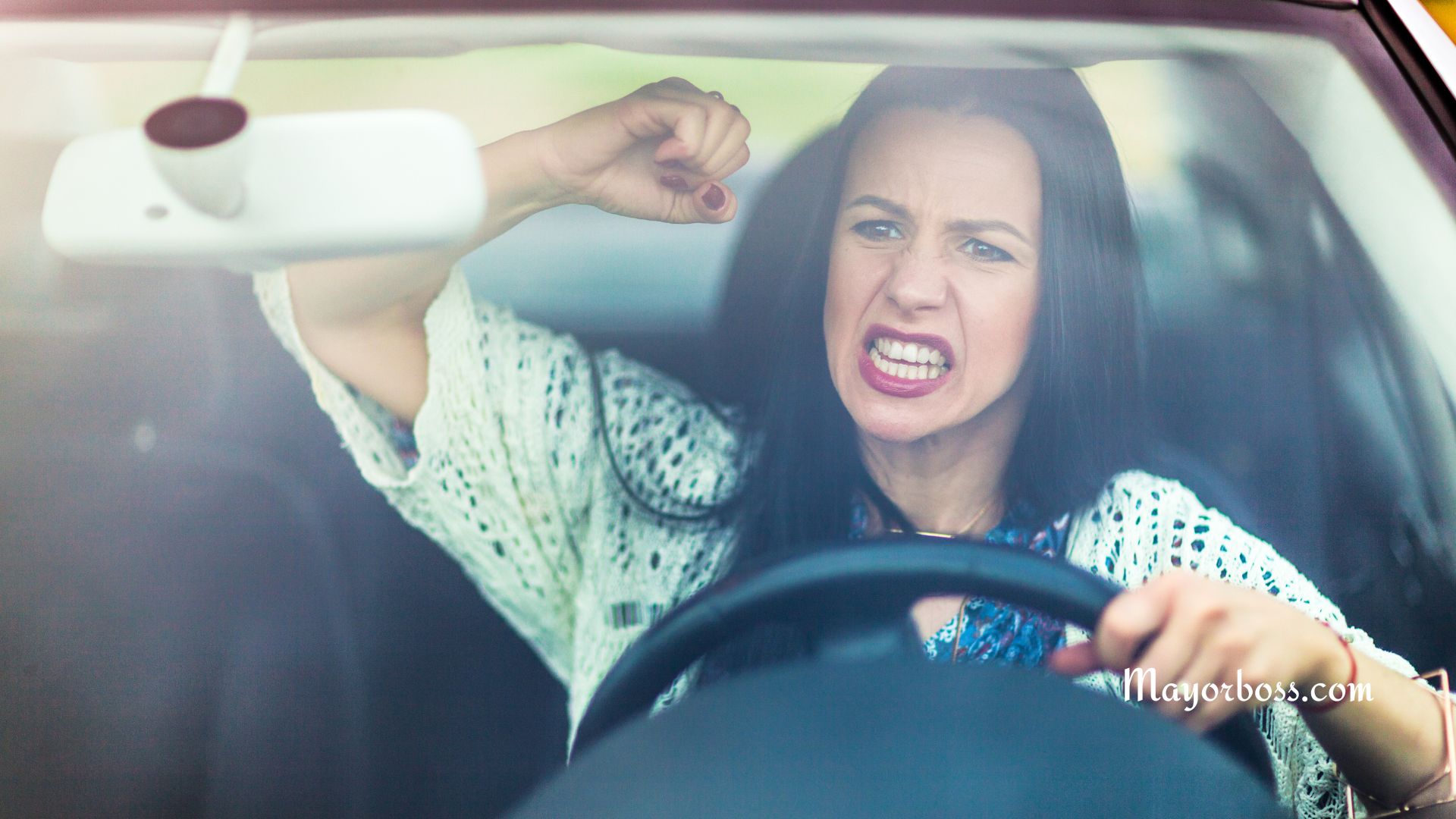

1. Your Heart Rate Increases
One of the first things that happen when you get angry is that your heart rate increases. Actually, this response is part of your body’s “fight or flight” reaction to perceived threats. Your body releases adrenaline, which in turn quickens your heartbeat. This rapid heart rate can put a lot of stress on your cardiovascular system if not managed properly.
2. You Might Start to Sweat
Additionally, anger often causes an increase in body temperature. From subtle annoyance to full-blown rage, your body responds to the heat of anger by producing sweat. This process is your body’s attempt to cool down and maintain a stable internal temperature. While not immediately dangerous, excessive sweating can lead to dehydration if not addressed.
3. Your Breathing Becomes Rapid
And if your heart rate and body temperature aren’t enough, anger can also speed up your breathing. When you’re angry, your body is preparing to either confront the threat or run away from it. To fuel these potential actions, your body needs more oxygen, so your breathing rate increases. But prolonged periods of rapid breathing can lead to a condition known as hyperventilation, which can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or even fainting.
4. Muscles Tense Up
In fact, scientists believe anger can also cause your muscles to tense up. Your body, while preparing for the ‘fight or flight’ response, tightens its muscles, ready for immediate action. This can lead to feelings of stiffness, especially in your neck and shoulders. Those who often experience anger might suffer from chronic muscle tension, leading to recurring discomfort or pain.
5. Your Digestive System is Impacted
Anger has nothing to do with digestion, right? Wrong! In the end, when you’re angry, your body diverts energy and resources away from processes like digestion to focus on dealing with the immediate ‘threat.’ This can lead to stomach discomfort, decreased appetite, or even digestive disorders over time.
6. Changes in Your Brain
The effects of anger are not limited to your physical body; they also impact your brain. When you’re angry, your amygdala, the part of the brain responsible for emotional responses, becomes more active. In the end, this heightened activity can lead to impulsive and poor decision-making.
In addition to the amygdala, prolonged anger can cause changes in your prefrontal cortex, the area responsible for decision-making and judgment. Chronic anger might result in difficulties with thinking and reasoning, which can impact your everyday life.
Conclusion
Regardless of how often you experience anger, it’s clear that it has a significant impact on your body. From increased heart rate to muscle tension, the effects are extensive and interconnected. For that reason, managing anger is crucial not only for your emotional health but also for your physical well-being.
In the first place, understanding the physical manifestations of anger can help you identify when you need to employ stress-reducing techniques. It might also be beneficial to seek professional guidance if you’re struggling to manage anger on your own.
And always remember to take care of your body – it’s the only one you have. Less or more, anger is a natural human emotion. But it’s how you handle it that truly matters. Your body will thank you for it.
Further Reading: 15 Ways to Calm Down When Angry