Itchy, Burning, or Uncomfortable Down There? It Could Be a Yeast Infection
What Is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
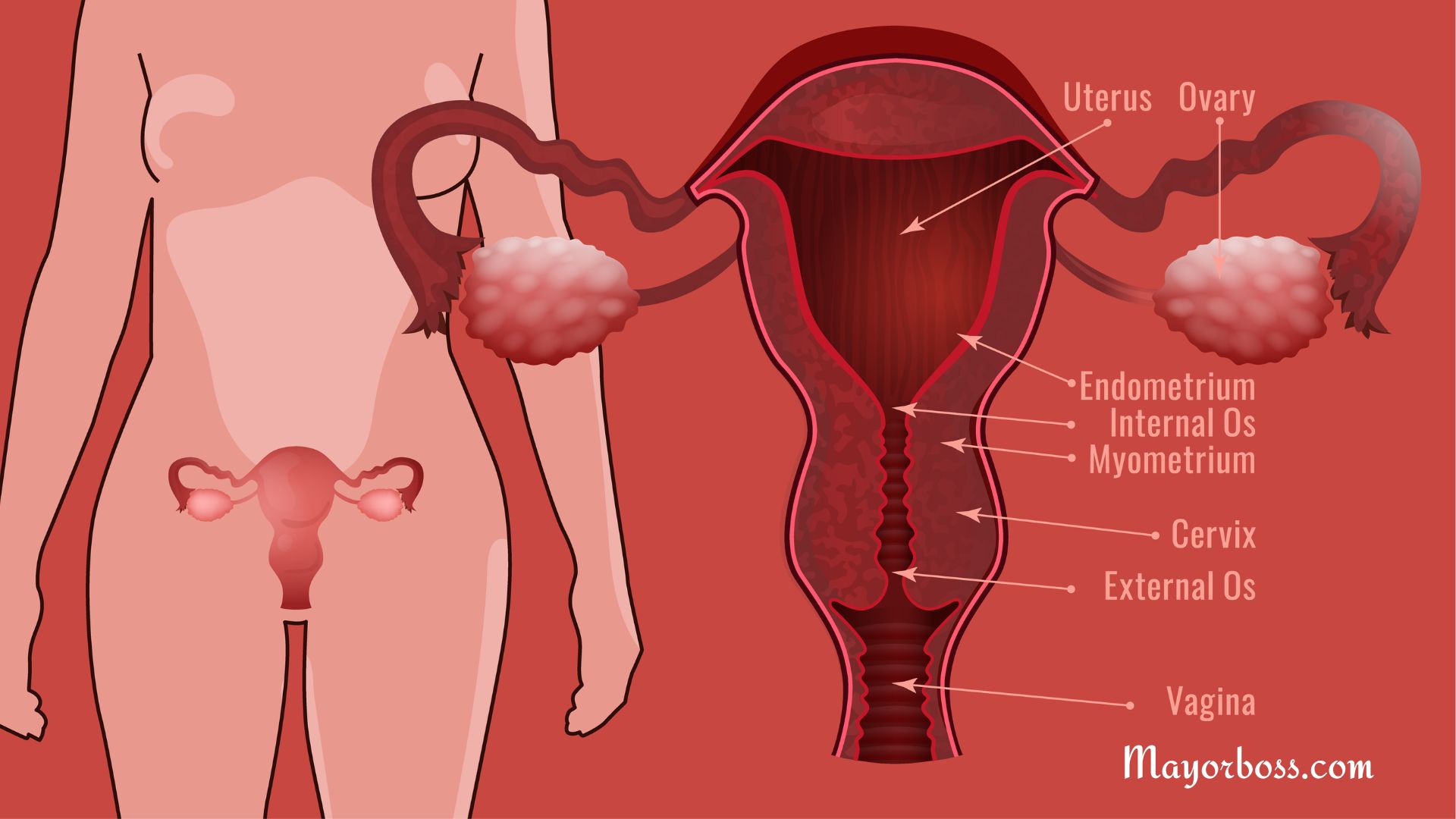
A vaginal yeast infection, also called vaginal candidiasis or thrush, happens when there’s an overgrowth of yeast (usually Candida albicans) in the vagina. Yeast naturally lives in the vagina in small amounts, along with bacteria. But when something upsets that balance, the yeast can multiply and cause itching, burning and abnormal vaginal discharge.
It’s common. Most women will experience it at least once in their lives. For some, it may happen more than once a year.
Common Symptoms

Yeast infections can be uncomfortable. The symptoms may worsen a few days before your period begins. They often bring one or more of the following symptoms:
- Itching inside or around the vagina
- Burning, especially during urination or sex
- Thick white discharge that looks like cottage cheese
- Redness or swelling of the vulva
- Soreness or irritation
Some women may have only mild symptoms. Others might find the discomfort hard to ignore. If you’re feeling itchy, irritated, or have unusual discharge, don’t ignore it. It could be a yeast infection.
What Causes It?
Several things can cause the yeast in your vagina to grow too much. These include:
- Antibiotics: They kill bacteria, including the good kind that keep yeast in check.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, or birth control pills can shift the vaginal balance.
- Tight or non-breathable clothing: Moisture and warmth around the vagina can create the perfect setting for yeast.
- High blood sugar levels: Women with diabetes are more likely to get yeast infections, especially if their blood sugar isn’t well controlled.
- Weakened immune system: Illness or certain medications can reduce your body’s ability to keep yeast under control.
- Douching or scented products: These can upset the vagina’s natural balance.
How It’s Diagnosed
If you suspect a yeast infection, it’s important to get the right diagnosis—especially if it’s your first time. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and may take a sample of your vaginal discharge to confirm what’s going on.
Many women try to treat themselves at home, but symptoms like itching and discharge can also be caused by other infections, such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections (STIs). That’s why checking with a healthcare provider is wise.
Treatment
Yeast infections are usually easy to treat. The most common treatments include:
- Antifungal creams or suppositories: These go inside the vagina or on the skin around it. They may be available over the counter or prescribed.
- Oral antifungal pills: A single dose of fluconazole is often enough for many cases. Your doctor will decide what’s best based on your symptoms.
Some treatments work in one day. Others take 3 to 7 days. Always finish the full treatment, even if you feel better earlier.
Can It Come Back?
Yes. Some women get recurring yeast infections—four or more in a year. When that happens, your doctor may recommend longer treatment, possibly over several months. They’ll also look for underlying reasons, like uncontrolled diabetes or hormone changes.
How to Prevent It
While not all yeast infections are preventable, you can lower your risk:
- Wear breathable cotton underwear
- Avoid tight pants or leggings that trap moisture
- Don’t use scented soaps or vaginal sprays
- Change out of wet clothes quickly, like after a swim or workout
- Wipe from front to back to prevent spreading yeast or bacteria
- Keep blood sugar under control if you have diabetes
Also, skip douching. The vagina cleans itself naturally, and douching disrupts its healthy environment.
When to See a Doctor
It’s time to call your doctor if:
- It’s your first yeast infection
- You’re unsure if your symptoms are from yeast
- Symptoms come back after treatment
- You have four or more infections in one year
- You’re pregnant or have other health concerns