What Causes Itching?
Itching, also known as pruritus, is a common sensation that compels us to scratch. It can be localized, affecting just one area, or generalized, occurring all over the body. Sometimes itching can feel like pain, according to the National Institutes of Health. While often linked to skin conditions, itching can also indicate other medical issues. Let’s dive into the possible causes and how to alleviate it.
Understanding Itching
According to Dr. Natalia Hapych, a respected family doctor, “Itching can be the result of a variety of causes, from everyday environmental factors to serious underlying medical conditions. It is our body’s way of telling us that something may not be right.”
You’ve probably experienced an itch you couldn’t scratch. While irritating, most itching is not indicative of a serious health problem. However, it can drastically affect your quality of life, particularly if it is persistent or widespread.
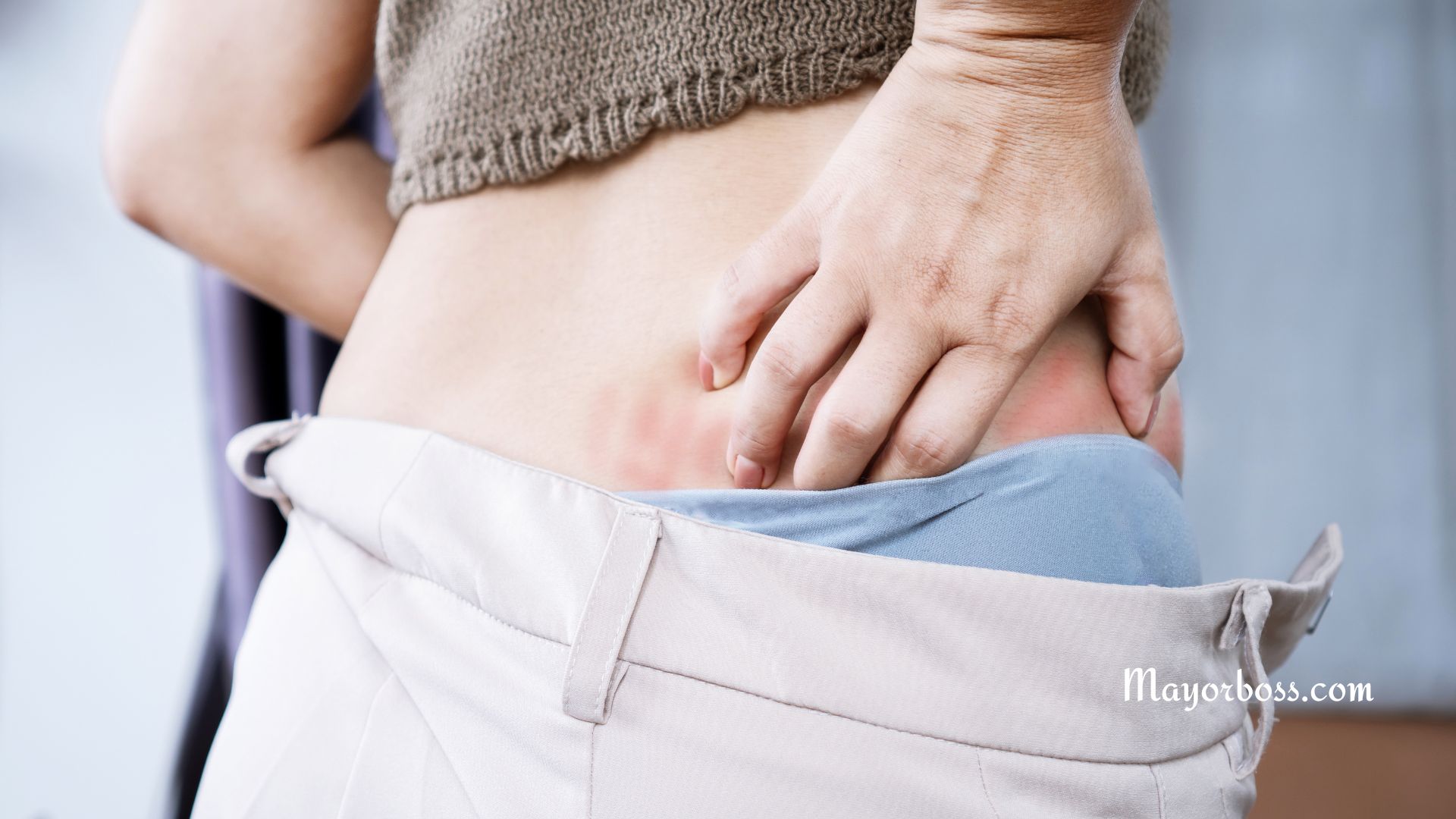

Common Causes of Itching
Itching can be triggered by various factors. Here are some common causes you should be aware of:
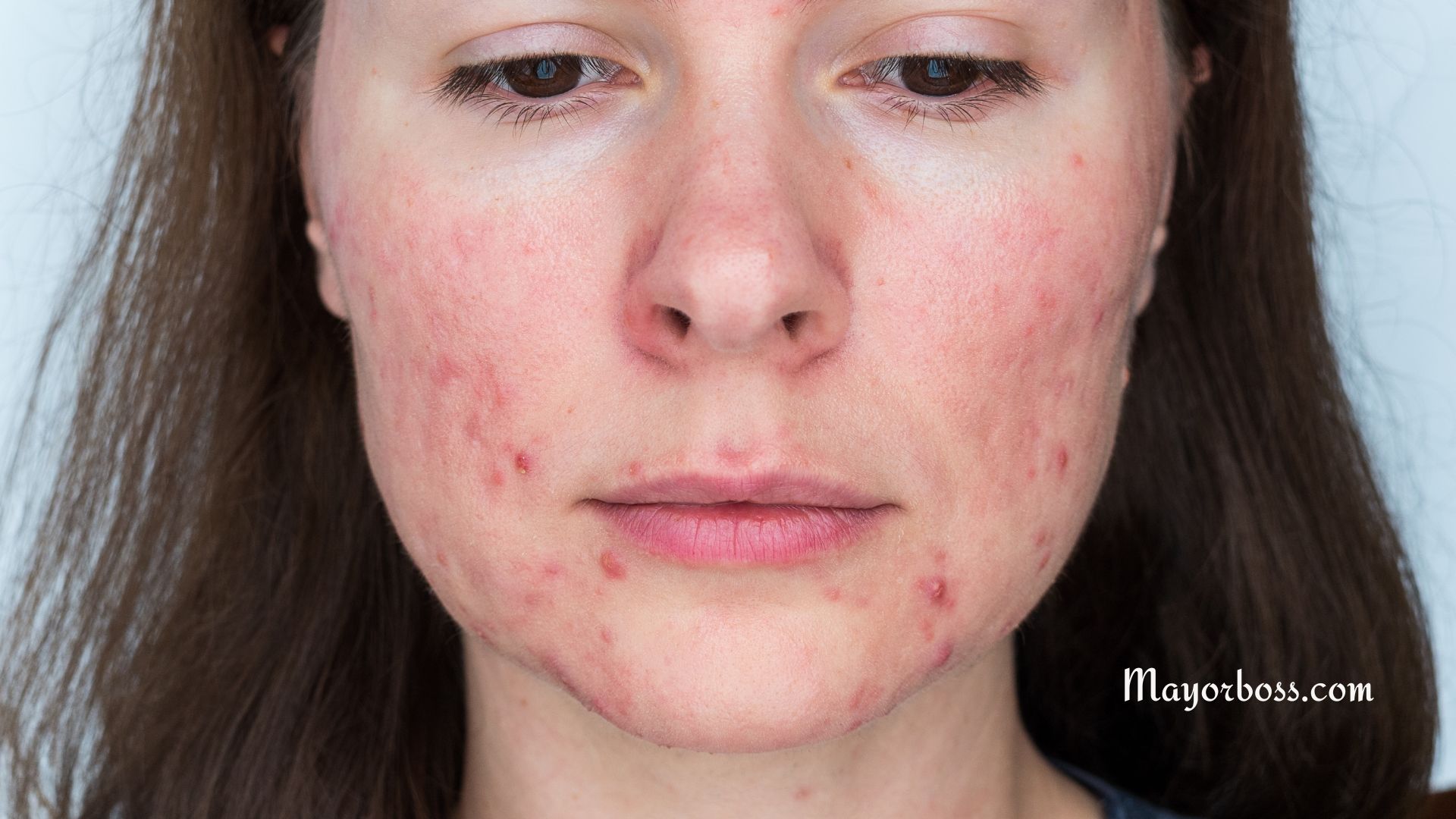
- Skin Conditions: Eczema, psoriasis, and hives are common skin conditions that can cause intense itching.
- Insect Bites and Parasitic Infections: Bug bites, scabies, or lice infestations can lead to severe itching.
- Allergies: Certain foods, medicines, cosmetics, irritating chemicals, or contact with specific substances can provoke an allergic reaction, causing itchiness.
- Dry Skin: In the absence of a visible rash or skin disease, you might be dealing with xerosis (dry skin), a common cause of itching, particularly in older adults or during the winter months.
Less Common But Serious Causes
In some cases, itching may signal more serious health conditions. These can include:
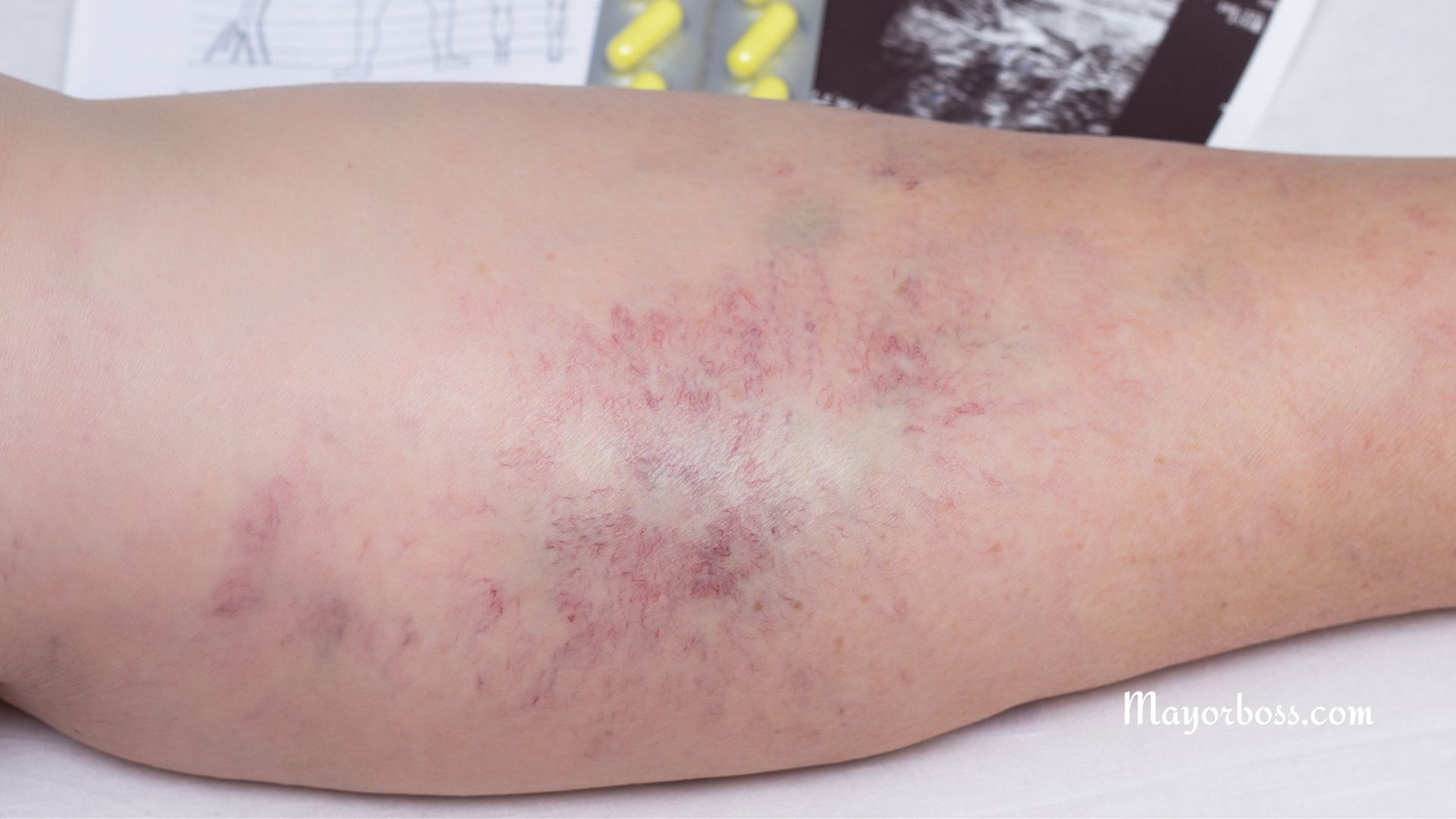
- Liver disease: Chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis can cause itching.
- Kidney failure: Patients undergoing dialysis often report itching.
- Thyroid disorders: Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can both lead to itching.
- Cancers: Certain types of cancers, such as lymphoma, can cause itching.
“Despite being less common, these causes are significant,” warns Dr. Hapych. “If you experience persistent itching without a clear cause, it’s important to see a healthcare provider.”
Treating and Preventing Itching
While itching can be bothersome, there are numerous treatments and preventive measures you can take:
- Moisturize Regularly: For dry skin, applying a high-quality moisturizer after bathing can be beneficial.
- Avoid Irritants: If you’re allergic to certain substances, try to avoid contact with them.
- Over-the-counter Treatments: Antihistamines, corticosteroid creams, or calamine lotion can help alleviate itching.
- Cool Down: Applying a cold, damp cloth or ice pack to the area can provide relief.
However, these measures are most effective for itching due to minor causes. For severe or persistent itching, medical intervention might be necessary.
When to See a Doctor
Dr. Hapych emphasizes, “You should see a doctor if your itching is severe, doesn’t improve after two weeks, affects your whole body, or is accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue, weight loss, or changes in bowel movements or urination. It’s crucial not to ignore these signs, as they could indicate a more serious underlying condition.”
To conclude, while itching is common and often harmless, persistent or severe itching warrants medical attention.
Further Reading: Relief for Itchy Skin: An Expert’s Guide