The Flu Vaccine: Your Shield Against Influenza
The flu vaccine is your best defense against the seasonal flu. It trains your immune system to recognize and fight the influenza virus, reducing your risk of getting sick. While it’s not 100% effective, it can lessen the severity of symptoms if you do catch the flu. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the vaccine is especially important for certain groups like young children, elderly people, and those with compromised immune systems.
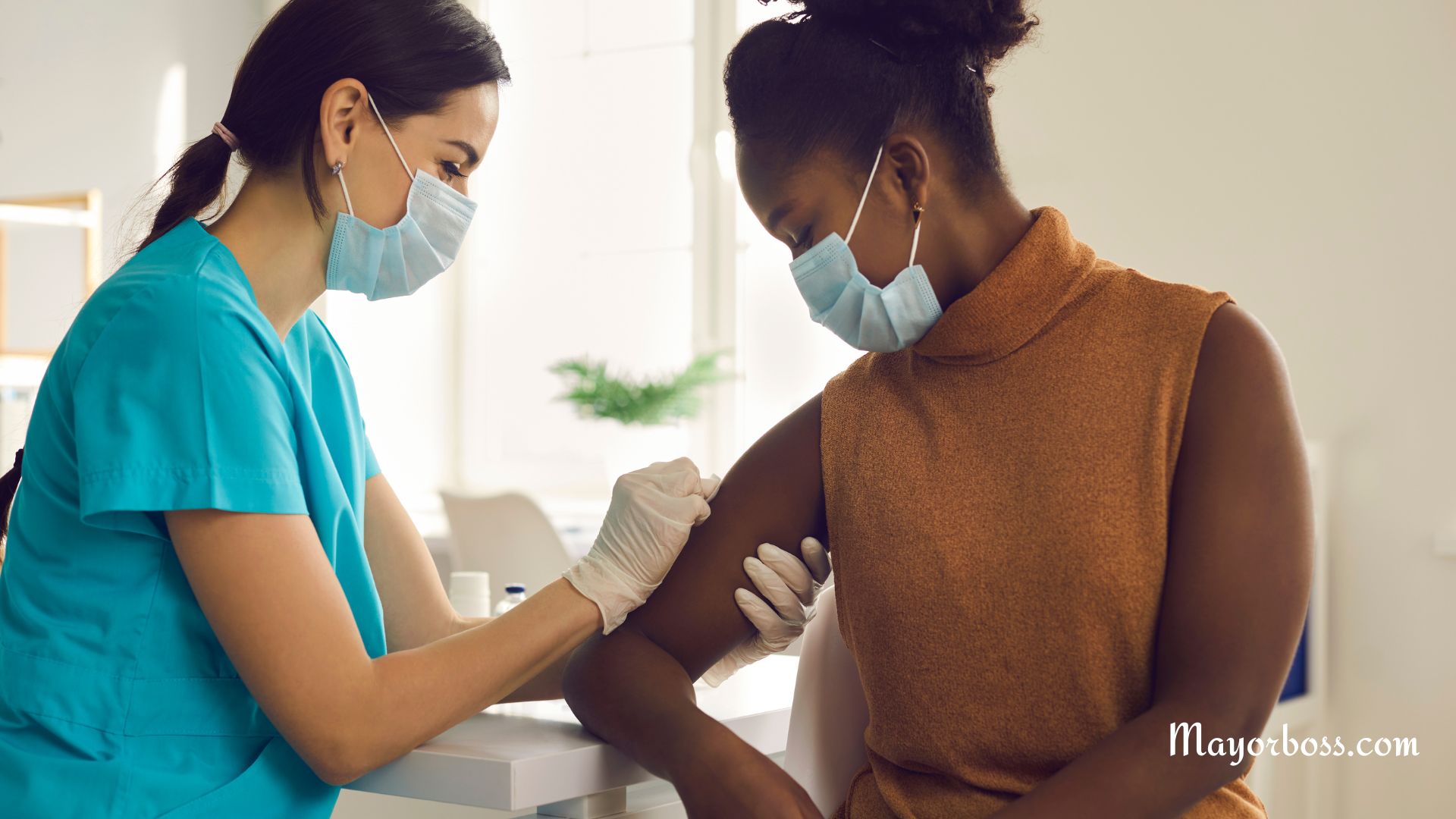

Why Get the Flu Vaccine?
You might wonder why you should get a flu shot every year. Well, the flu isn’t just a bad cold; it’s a serious illness that can lead to complications such as pneumonia, hospitalization, and even death. The vaccine works by introducing a small, harmless piece of the virus into your body. This prompts your immune system to produce antibodies, which can fend off the real virus if you’re exposed to it later.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
Almost everyone over the age of 6 months is recommended to get the flu vaccine. However, it’s crucial for:
- Young children (6 months to 5 years)
- Adults aged 65 and older
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with chronic health conditions like asthma, diabetes, or heart disease
When Should You Get Vaccinated?
In general, the best time to get the flu vaccine is before flu season starts. In the United States, flu season typically runs from October to May. So, it’s a good idea to get vaccinated in early fall. If you miss this window, don’t worry; getting vaccinated later can still offer protection.
Types of Flu Vaccines
There are various types of flu vaccines available:
Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (IIV)
This is the most common type and is given via injection.
Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV)
This is a nasal spray and is generally recommended for healthy people between the ages of 2 and 49.
High-Dose Vaccine
This is specifically designed for people 65 years and older and contains four times the amount of antigen, the part of the vaccine that prompts the body to make antibodies.
How Effective is the Vaccine?
While the flu vaccine won’t guarantee you’ll avoid the flu, it can significantly reduce your risk. Its effectiveness can vary depending on several factors, such as the age and health of the person getting vaccinated and how well the vaccine matches the circulating virus strains. However, even if you do get the flu after vaccination, your symptoms are likely to be milder than if you hadn’t been vaccinated at all.
Possible Side Effects
After getting the flu shot, you might experience some mild side effects like:
- Soreness or redness at the injection site
- Low-grade fever
- Fatigue
These symptoms usually disappear within a couple of days.
Special Considerations
Allergies
If you’re allergic to eggs, there are egg-free versions of the vaccine available.
Chronic Conditions
In people with chronic conditions like asthma or heart disease, getting the flu vaccine is even more vital as the flu can exacerbate these conditions.
To Sum It Up
Getting vaccinated is a simple but effective way to protect yourself and those around you from the flu. While it’s not foolproof, it significantly lowers your risk of severe illness, complications, and spreading the virus to others. So, don’t delay; get your flu shot as soon as possible.