Don’t Ignore Left-Sided Chest Pain: Symptoms, Causes, and When to See a Doctor
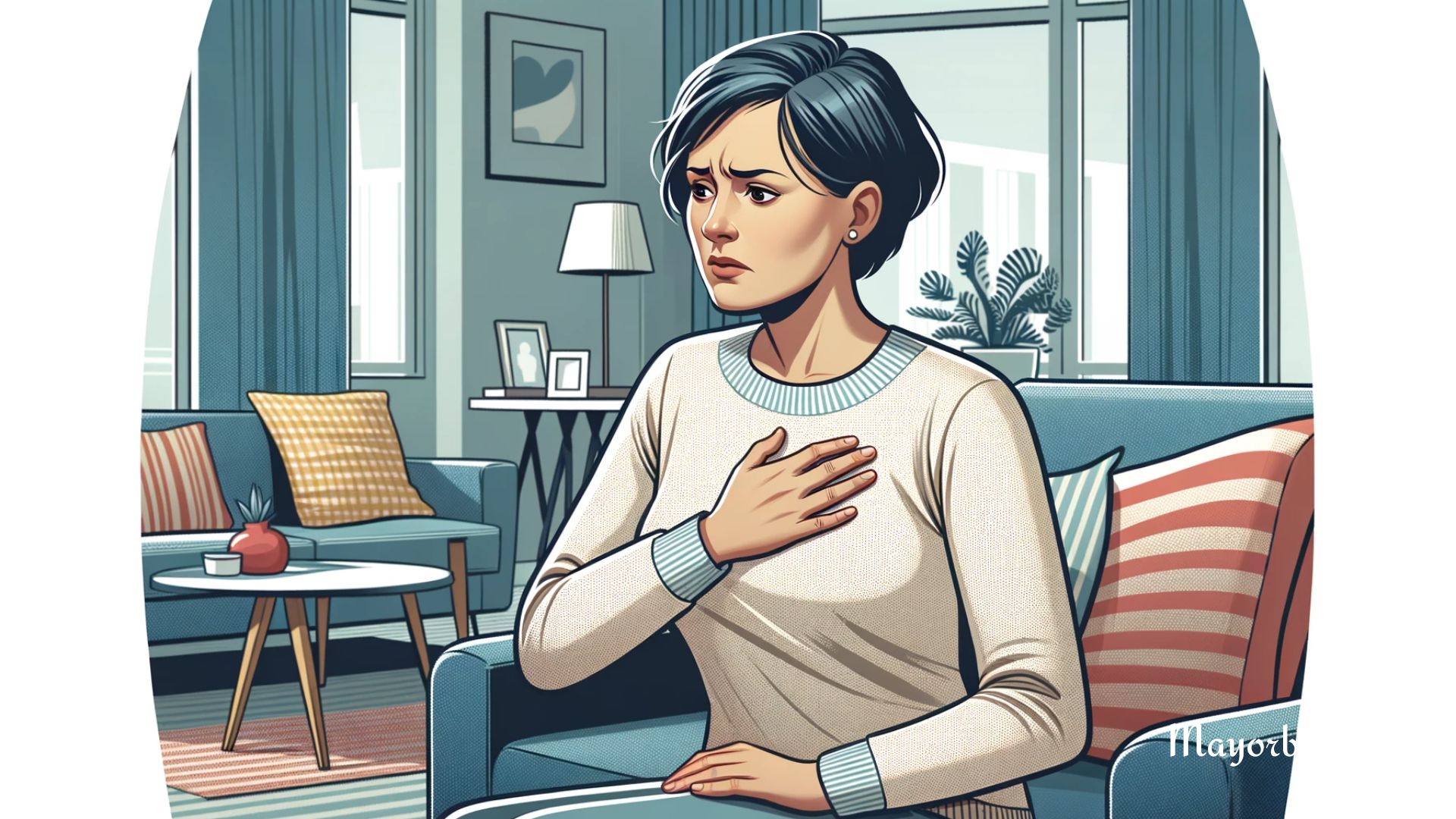
When you experience pain on the left side of your chest, it’s natural to feel alarmed. After all, this area is closely associated with the heart. However, not all left-sided chest pain is cardiac in origin. It’s essential to understand the various causes and symptoms and know when it’s time to consult a doctor. Let’s explore this important topic.

Symptoms and Causes of Left-Sided Chest Pain
Left-sided chest pain can arise from a variety of conditions, ranging from benign to life-threatening. It’s crucial to pay attention to the nature of the pain and accompanying symptoms to determine its seriousness.
Cardiac Causes
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): Often the first thought when left-sided chest pain occurs. The pain is usually severe, can feel like pressure or a squeezing sensation, and may radiate to the arm, neck, or jaw.
- Angina: Caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina pain can mimic heart attack pain but often occurs with exertion and resolves with rest.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the lining around the heart, causing sharp, stabbing pain that may worsen with breathing or lying down.
Non-Cardiac Causes
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Acid reflux can cause a burning sensation or pain in the chest.
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Strained muscles or ribs can cause chest pain, often worsened by certain movements or deep breathing.
- Pulmonary Causes: Conditions like pneumonia or a pulmonary embolism can manifest as chest pain, often accompanied by breathing difficulties.
- Stress and Anxiety: Panic attacks can produce chest pain similar to cardiac pain, along with symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, and shortness of breath.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Sudden, severe chest pain
- Chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or dizziness
- Pain that radiates to other areas like the arm, neck, or jaw
- New or worsening symptoms
Identifying Red Flags
It’s better to err on the side of caution with chest pain. Certain red flags, like pain that doesn’t improve with rest or is associated with physical exertion, should prompt an urgent medical evaluation.
Treatment Options
Treating Cardiac Causes
- Heart Attack:
- Emergency Care: Immediate medical intervention with medications like aspirin and other clot-busting drugs.
- Long-term Management: Lifestyle changes, medication for heart function and cholesterol, and possibly surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
- Angina:
- Medications: Nitrates like nitroglycerin to relieve pain, beta-blockers, or calcium channel blockers for prevention.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Pericarditis:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and, in severe cases, colchicine or corticosteroids.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups to ensure the inflammation doesn’t recur.
Treating Non-Cardiac Causes
- GERD:
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoid foods that trigger acid reflux, eating smaller meals, and not lying down after eating.
- Medication: Antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors.
- Musculoskeletal Issues:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the chest muscles.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers and heat or cold therapy.
- Pulmonary Causes:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like pneumonia.
- Blood Thinners: In the case of pulmonary embolism.
- Stress and Anxiety:
- Psychotherapy: Techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy.
- Medications: Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
While not all causes of left-sided chest pain are preventable, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of cardiac issues. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding smoking.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial, especially if you have risk factors for heart disease. Early detection and management of conditions like hypertension and high cholesterol are vital.