Understanding the Female Reproductive System
What is the Female Reproductive System?
The female reproductive system is an intricate and vital part of a woman’s body. It plays a crucial role in the reproductive process, which includes menstruation, fertilization, and childbirth.
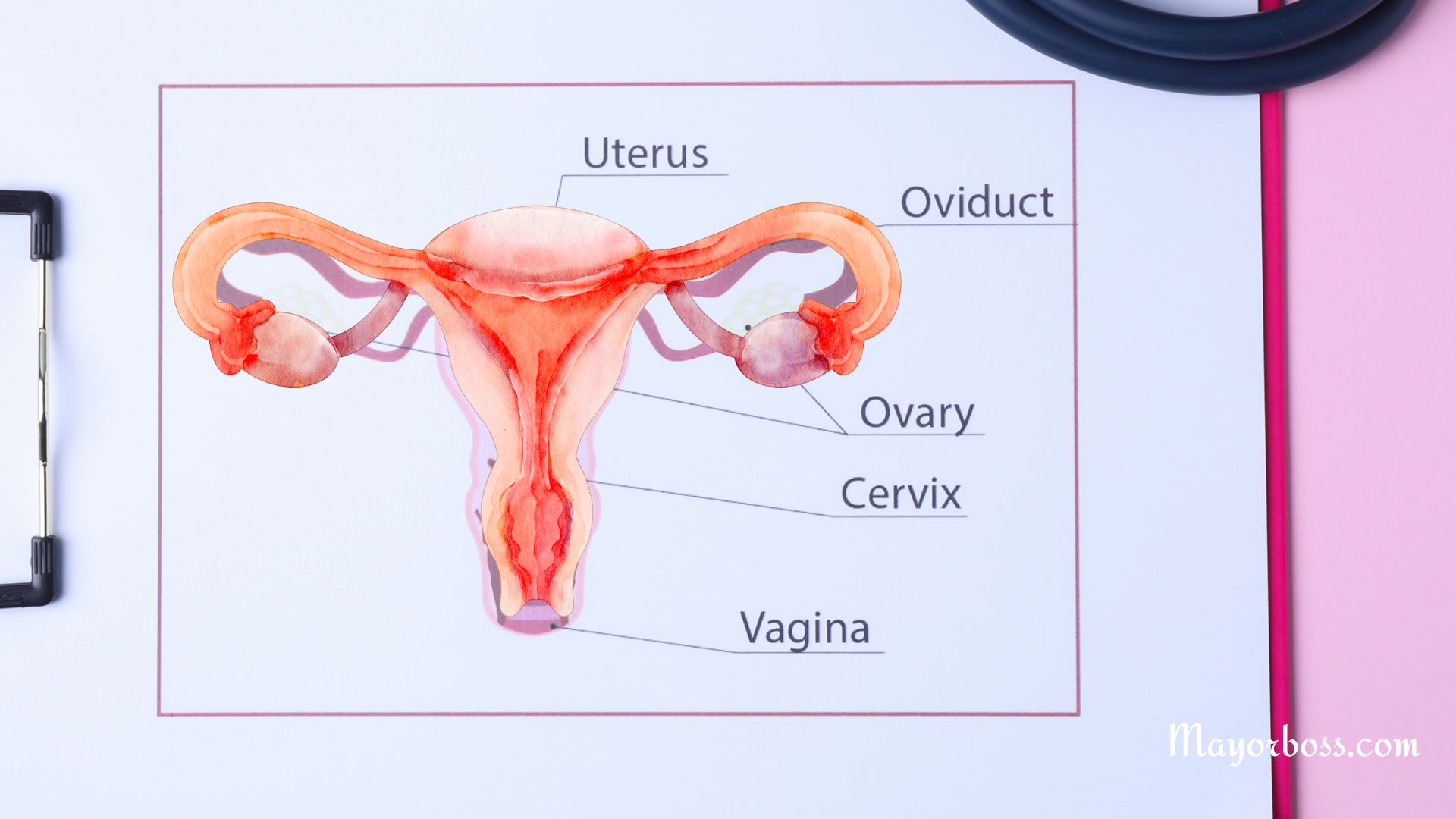
Key Components of the Female Reproductive System
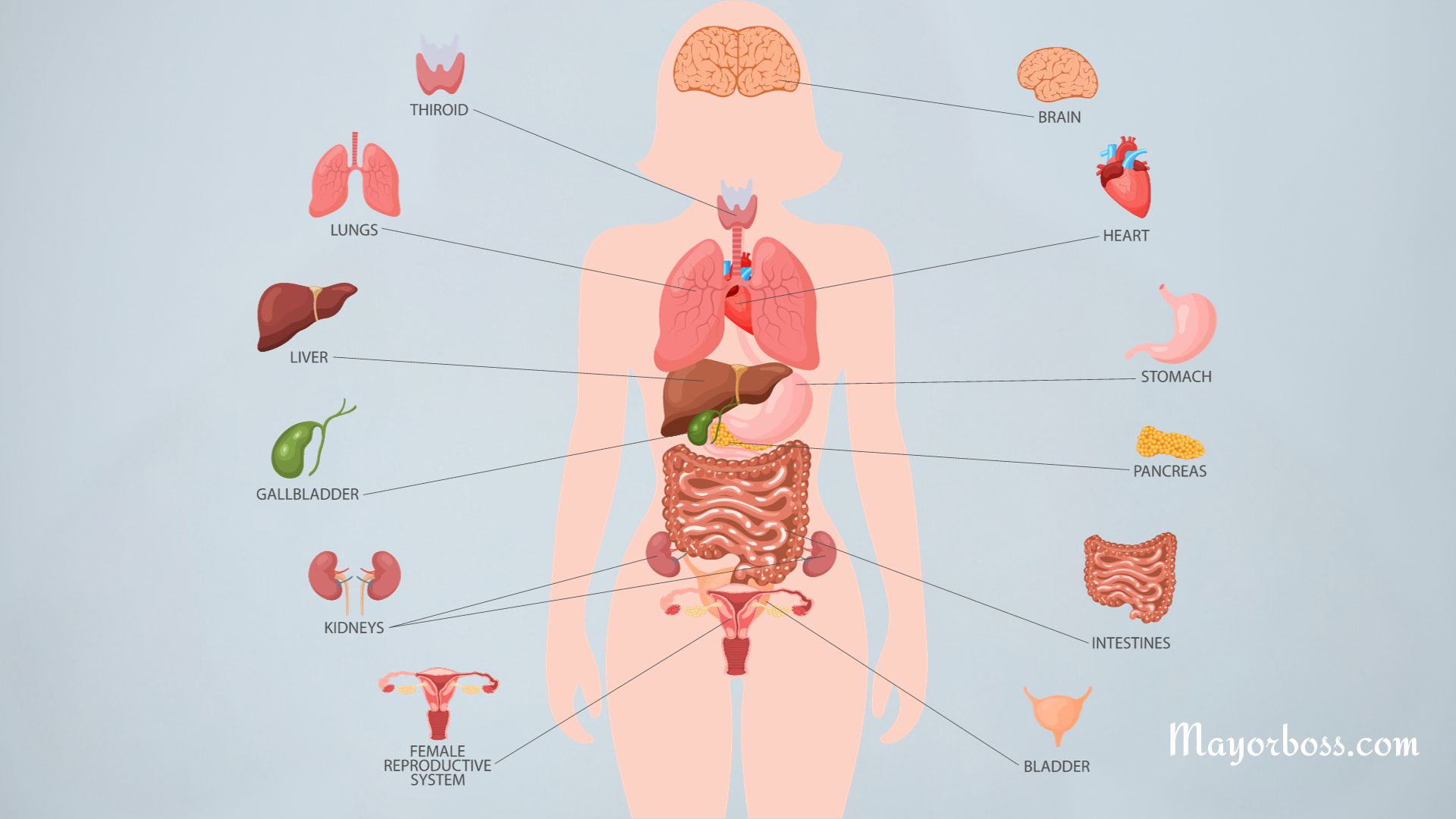
- Ovaries: These are small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. Ovaries are responsible for producing eggs (ova) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tubes: These tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus. After an ovary releases an egg, the fallopian tube helps guide it toward the uterus. Fertilization, where a sperm meets an egg, typically occurs in one of these tubes.
- Uterus (Womb): The uterus is a pear-shaped organ where a fertilized egg grows into a fetus. It’s lined with a special tissue called the endometrium, which is crucial for pregnancy.
- Cervix: This is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. During childbirth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through.
- Vagina: Often referred to as the birth canal, the vagina is a muscular tube that extends from the cervix to the vulva. It’s involved in sexual intercourse, childbirth, and the passing of menstrual blood.
Functions of the Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle: This monthly cycle prepares the body for pregnancy. If fertilization doesn’t occur, the lining of the uterus sheds through menstruation.
- Ovulation: This is the process where an ovary releases an egg. It’s a critical part of the menstrual cycle.
- Fertilization: When a sperm successfully combines with an egg in the fallopian tube, fertilization occurs.
- Pregnancy: After fertilization, the embryo implants in the uterus, where it grows into a fetus.
- Hormone Regulation: The reproductive system produces hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which are vital for reproductive health and also influence other body systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the role of the female reproductive system in hormone production?
The ovaries produce hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone, which control the menstrual cycle, support pregnancy, and influence other body functions.
Can lifestyle choices impact the health of the reproductive system?
Absolutely! A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol can significantly benefit reproductive health.
How often should one have a reproductive health check-up?
Regular gynecological check-ups are essential. The frequency depends on age, health history, and specific medical advice from your healthcare provider.
Remember, maintaining reproductive health is vital not just for childbearing but also for overall well-being. If you have concerns about your reproductive health, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional.