What Causes Diarrhea After Eating?
Diarrhea after eating, or postprandial diarrhea, can be caused by a range of factors, including bacterial infections, food poisoning, stress, antibiotic use, and digestive disorders.
What is Diarrhea?
In most cases, diarrhea refers to a condition characterized by loose or watery stools. It can be accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and urgency.
Diarrhea after eating, specifically, may occur within a few hours after consuming food.
What causes diarrhea after eating?

Truth be told, there are so many factors that could cause diarrhea after eating.
For this reason, health experts strongly advise patients to identify the specific cause to manage it effectively.
Lactose intolerance
For many people, lactose intolerance can cause diarrhea after eating.
This means you may experience diarrhea after consuming dairy products, as your body may have difficulty digesting lactose, a specific sugar in milk and other dairy products.
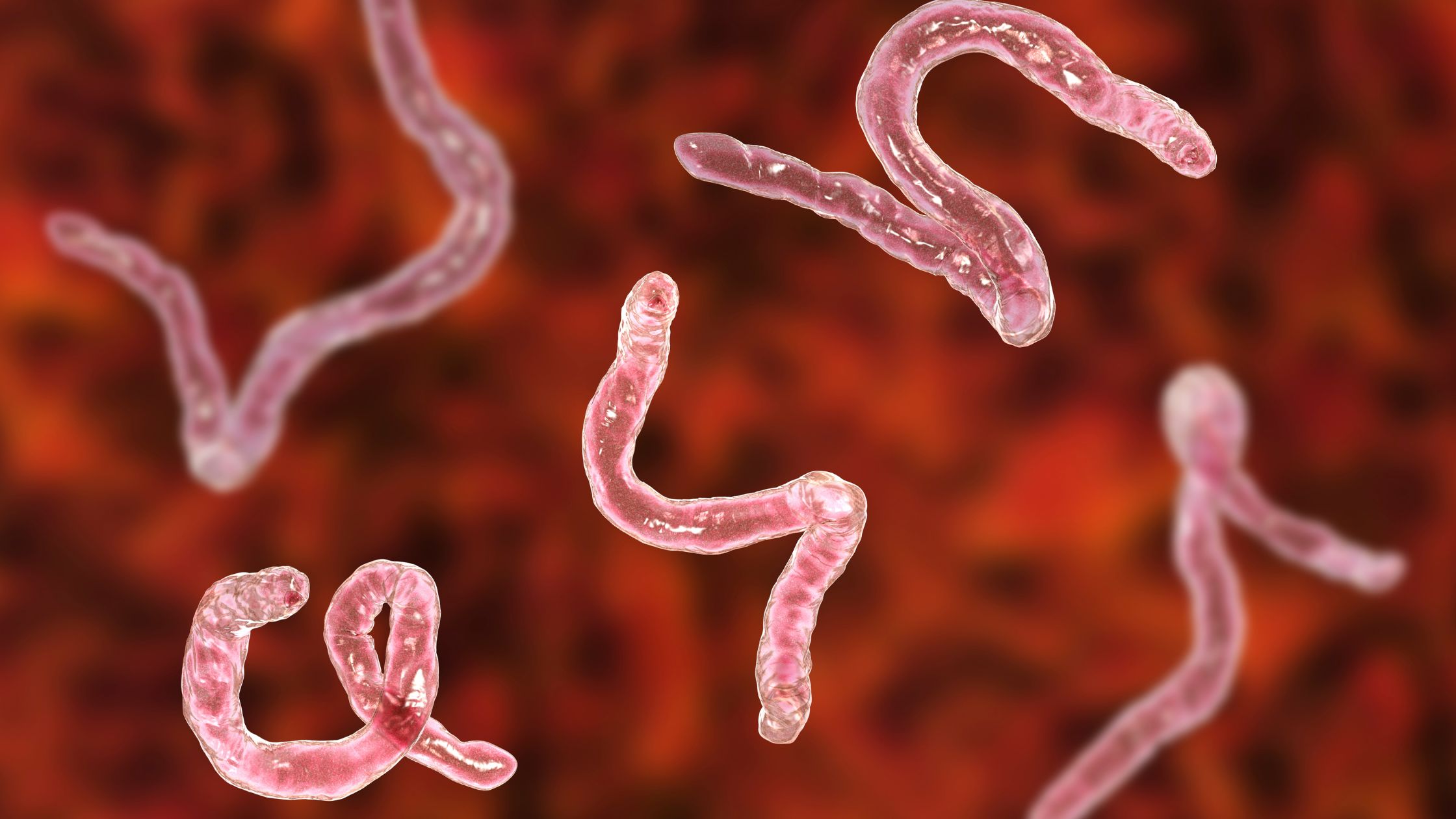
Parasites
In some cases, parasites can cause diarrhea after eating.
Most often, these parasites are acquired from contaminated water or food.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections can lead to diarrhea after eating.
Experts generally agree that common bacteria like Cryptosporidium, Shigella, E. coli, Yersinia, and Salmonella can cause foodborne illnesses that result in diarrhea.
Eating too much sugar
Eating too much sugar foods can sometimes cause diarrhea.
This may be because sugar draws water into the gut, which can lead to watery stools.
Food poisoning
Food poisoning is another common cause of diarrhea after eating.
It often results from consuming food contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites.
Certain medications
Certain medications, particularly antibiotics, and antacids containing magnesium, can cause diarrhea.
If you experience diarrhea after eating and taking medication, it might be a side effect.
Stress
Stress can manifest physically and may cause diarrhea after eating.
Therefore, if you’re feeling stressed or anxious, it could be contributing to your symptoms.
Eating certain foods
Some people may experience diarrhea after eating specific types of foods.
These can include high-fat foods, spicy foods, or foods high in fiber.
Drinking alcohol
Drinking alcohol, especially in excess, can irritate your digestive system and lead to diarrhea.
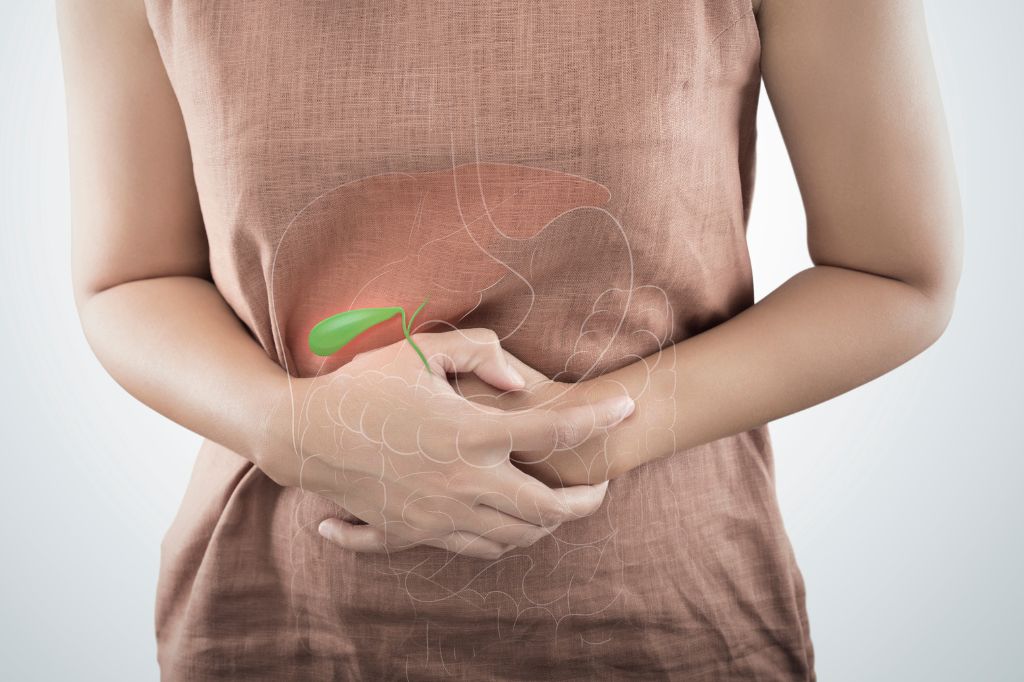
Gallbladder Issues
Gallbladder issues can also cause diarrhea, as the gallbladder plays a critical role in digestion by storing bile.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a lifelong condition that can cause a range of digestive symptoms, including diarrhea after eating.
Celiac disease
Celiac disease is an ailment where eating gluten causes damage to the small intestine, often resulting in chronic diarrhea.
Magnesium overdose
Magnesium overdose, often from supplements, can lead to diarrhea.
Therefore, always adhere to the recommended dosage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if I frequently get diarrhea after eating?
If you frequently experience diarrhea after eating, you should consult with a healthcare professional.
Chronic diarrhea could be a sign of an underlying health condition.
Therefore it’s essential to get a proper diagnosis to manage it effectively.
Can stress cause diarrhea after eating?
Yes, stress can cause diarrhea after eating.
When you’re stressed, your body goes into “fight or flight” mode, which can speed up your digestion and lead to diarrhea.
If you notice a correlation between stress levels and digestive problems, consider stress management techniques or discuss it with a health professional.
Can certain foods trigger diarrhea after eating?
Absolutely. Certain foods, like those high in fat, fiber, or spice, may trigger diarrhea in some individuals.
Moreover, food intolerances or allergies (like lactose intolerance or celiac disease) can cause diarrhea after consuming specific foods.
Is diarrhea after eating a sign of food poisoning?
It can be. Diarrhea is basically a common symptom of food poisoning, which occurs after consuming contaminated food.
If diarrhea is accompanied by other symptoms like vomiting, fever, or severe abdominal cramps, and if multiple people who ate the same food are experiencing these symptoms, it could be due to food poisoning.