Symptoms of Osteoporosis You Might Overlook
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease.” That’s because it can develop slowly, without any obvious symptoms at first. Many people don’t realize they have it until they break a bone. But your body may send early warning signs you might overlook. Paying attention to these symptoms could help you catch osteoporosis before it leads to serious damage.

What Is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become thin, weak, and brittle. It happens when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. This increases the risk of fractures, especially in the hips, spine, and wrists. It’s more common in older adults, especially women after menopause, but it can affect anyone.1
Early Signs Are Easy to Miss
Many symptoms of osteoporosis seem mild or unrelated to bone health. Here are some you should not ignore.
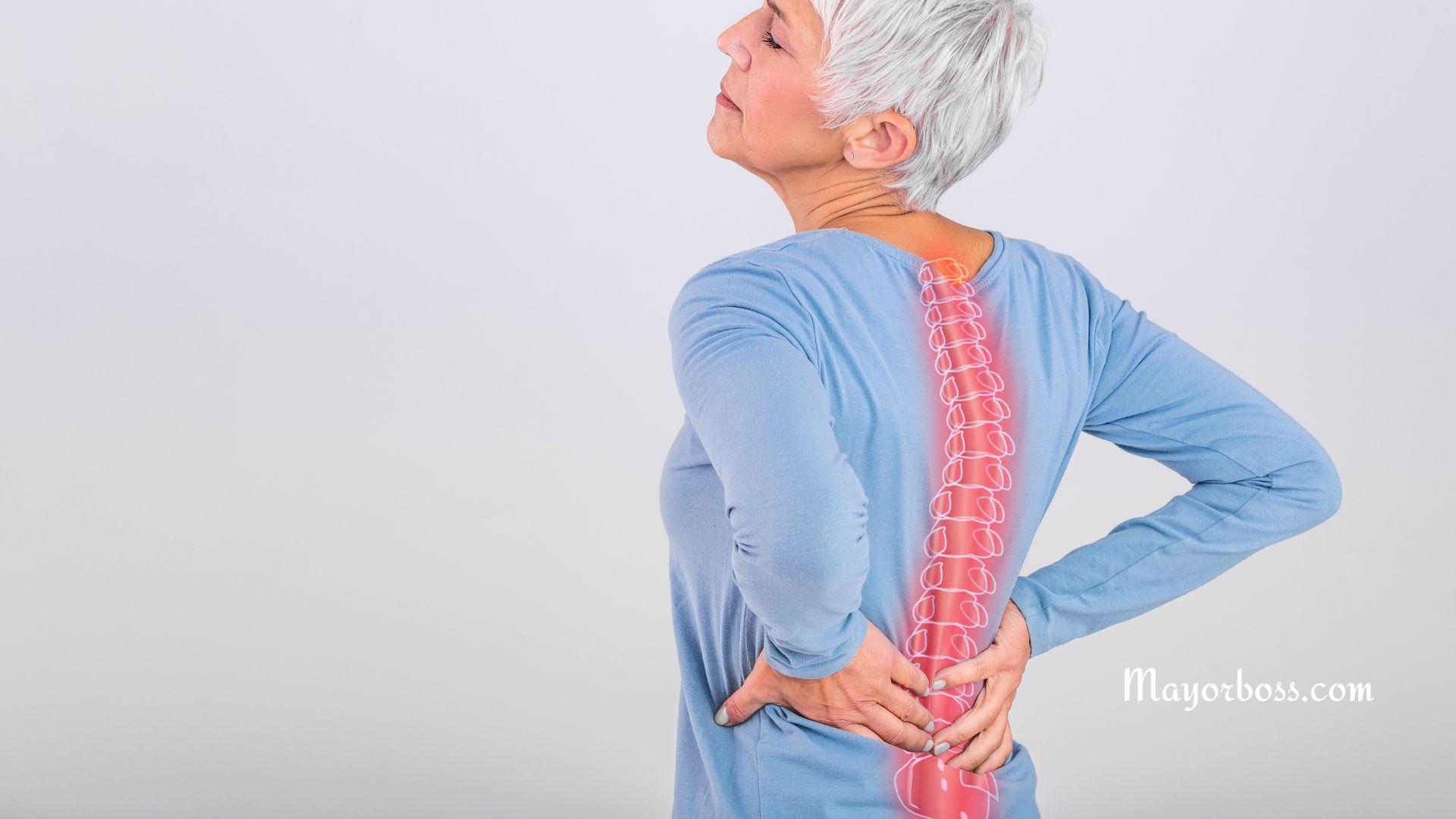
1. Back Pain That Won’t Go Away
Chronic back pain could be a sign of a compression fracture in the spine. These small fractures happen when weakened bones in the vertebrae collapse. The pain can come on slowly or suddenly. Some people feel it only when they stand or walk, but with some relief when they lie down. Others may have constant aching.2

2. Loss of Height Over Time
If your clothes seem longer or you’re suddenly looking up at people you once matched in height, take note. Shrinking more than one inch may be due to spine fractures from osteoporosis. These fractures compress the bones and cause you to lose height.
3. Stooped Posture or Hunched Back
A forward-leaning posture, often called a “dowager’s hump,” is a sign of vertebral fractures. As spine bones weaken and collapse, your back can curve forward. This may lead to trouble standing upright or moving freely.
4. Bone Fractures from Minor Falls
Breaking a bone after a minor fall or bump may seem unlucky, but it’s often a red flag. Healthy bones should not break easily. If you fracture a wrist, hip, or spine from something that wouldn’t normally cause harm, ask your doctor to check your bone density.
5. Weaker Grip Strength
Struggling to open jars or carry grocery bags? Research shows that weaker grip strength could be linked to lower bone density.3 While grip strength changes naturally with age, a sudden decline could be a sign your bones are also weakening.
6. Brittle or Weak Nails
Your nails may offer clues about your bone health. Weak, peeling, or brittle nails could reflect low calcium or bone density. Of course, nail changes can have many causes, but if they appear alongside other symptoms, it’s worth discussing with a doctor.
7. Receding Gums
Bone loss doesn’t only happen in your spine or hips. The jawbone can also lose density, causing your gums to recede. If your teeth seem longer or looser, or your dentist notices changes, it might be time to check your bones.
8. Shortness of Breath
As your spine compresses from vertebral fractures, it can reduce the space in your chest cavity. This makes it harder for your lungs to fully expand. As a result, you may feel short of breath even during mild activity.
Risk Factors Make Symptoms More Likely
Some people are more likely to develop osteoporosis and its hidden symptoms. Risk factors include:
- Being over 50
- Female sex, especially after menopause
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Low calcium or vitamin D intake
- Smoking or heavy alcohol use
- Inactive lifestyle
- Certain medications, like steroids or cancer treatments
If you have any of these risk factors and experience the symptoms above, don’t ignore them.4
What to Do If You Suspect Osteoporosis
Talk to your doctor. A bone density test, often called a DEXA scan, can show how strong your bones are. This test is painless and quick. Based on your results, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, supplements, or medication.5
References:
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/osteoporosis ↩︎
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoporosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351968 ↩︎
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6594500/ ↩︎
- https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/osteoporosis ↩︎
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/10683-dexa-dxa-scan-bone-density-test ↩︎