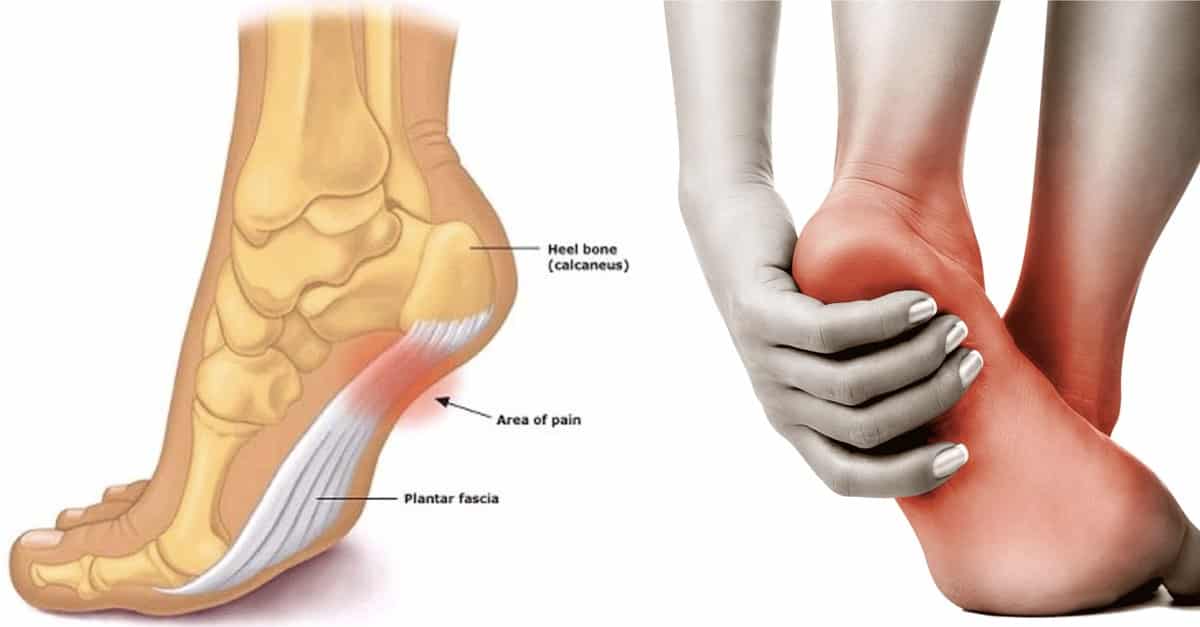
6 Early Signs of Gout to Never Ignore
Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by intense pain, redness, and swelling in joints, commonly in the big toe. Early warning signs may include bouts of discomfort, skin discoloration, and heightened sensitivity. Being aware of these symptoms can aid in early diagnosis and effective treatment.
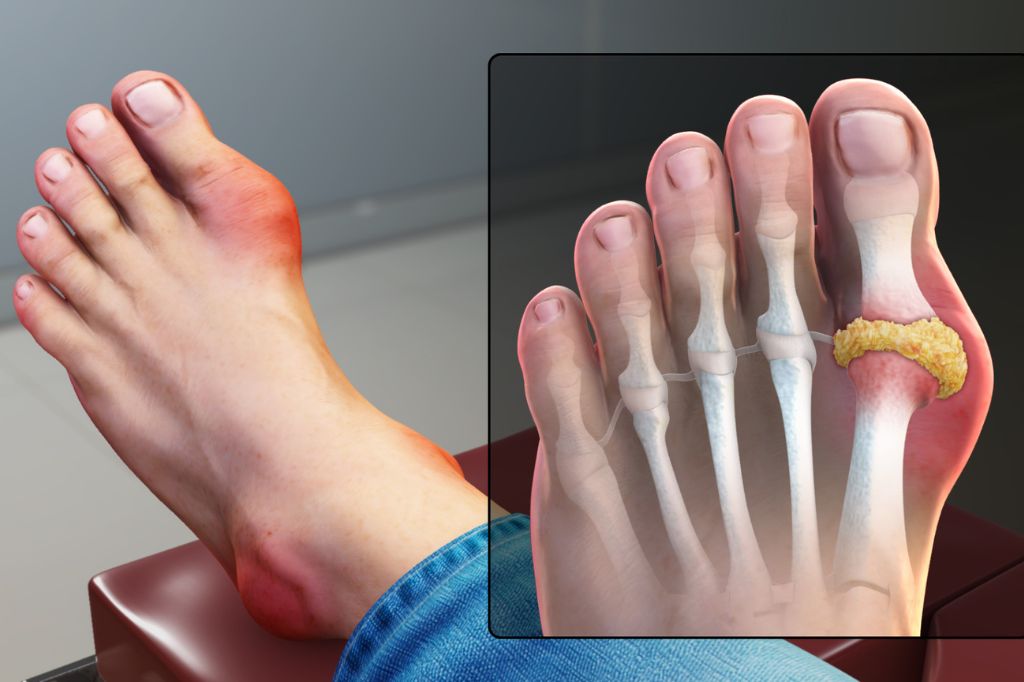
Sudden and Severe Pain in a Joint
The hallmark symptom of gout is excruciating pain that comes on suddenly, often in the middle of the night. If you wake up to a joint, usually your big toe, feeling like it’s on fire, this could be a sign of gout. The pain typically peaks within the first 4 to 12 hours. Clinically proven treatments, such as anti-inflammatory medications, can help manage this pain.
Redness and Warmth Over the Affected Area
Soon after the pain starts, you might notice the skin over the joint turning red and feeling warm to the touch. This happens because gout causes inflammation in the joint, which in turn causes these symptoms. When you notice this, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis.
Limited Range of Motion
Following the onset of pain and inflammation, you’ll likely find it hard to move the affected joint. This limited range of motion is another indicator of gout. Examples of movements that could be restricted include bending your toe or even just walking. Effective treatment often involves medications that reduce inflammation, thus improving your range of motion.
Swelling Around the Joint
Besides causing pain and limiting your movement, gout usually also leads to swelling around the affected joint. The inflamed area can look puffy and feel tender. According to healthcare experts, this swelling is due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joint, which triggers your body’s inflammatory response.
Tenderness and Heightened Sensitivity
If even the weight of a blanket or the touch of a sheet causes discomfort, you’re likely experiencing heightened sensitivity in the area. This tenderness is another sign you shouldn’t ignore. Anti-inflammatory medications and other treatments can often alleviate this symptom, helping you feel more comfortable.
Unexplained Fatigue and Malaise
Although not as common as the other symptoms, some people with gout also report feeling unusually tired or unwell. These feelings of general malaise can precede the more intense symptoms. So, if you’re feeling fatigued and also have other symptoms on this list, it would be wise to seek medical advice for a comprehensive evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Gout in the First Place?
Gout arises from high levels of uric acid in your body. This uric acid forms crystals that get deposited in joints, leading to inflammation and pain. Factors that can contribute to elevated uric acid levels include a diet rich in purines (found in red meat and seafood), excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
How Is Gout Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of gout usually involves a combination of clinical evaluation and tests. Your healthcare provider may recommend a joint fluid test to look for uric acid crystals or blood tests to measure uric acid levels. Imaging tests like X-rays can also provide valuable information, although they’re generally more useful for assessing long-term joint damage.
Are There Any Effective Home Remedies for Gout?
While it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a definitive diagnosis and treatment plan, some home remedies can provide temporary relief. Applying an ice pack to the affected area and elevating the joint can reduce inflammation. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding foods high in purines can also help manage symptoms.
Can Gout Lead to Other Health Issues?
Yes, if left untreated, gout can result in long-term complications. These may include chronic arthritis, joint deformities, and even kidney stones. According to medical experts, gout is also associated with other health conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease, making it essential to manage this condition effectively.
How Can I Prevent Future Gout Flare-Ups?
Preventing future episodes of gout involves lifestyle changes and, often, medication. Lowering uric acid levels through a balanced diet low in purines is a good starting point. Clinically proven medications like allopurinol can also help keep uric acid levels in check. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight are additional ways to reduce the risk of gout flare-ups.
Further Reading: 4 Trigger Foods For Gout