Inflammation: What You Need to Know
Summary: Inflammation is your body’s natural response to protect itself against harm. It’s a crucial part of the healing process, whether it’s due to an injury, an infection, or a toxin. When your body senses these dangers, it sends out a troop of white blood cells to surround and protect the area, hence forming visible redness and swelling. However, sometimes inflammation can become chronic, lasting for months or even years, which can lead to other health problems.
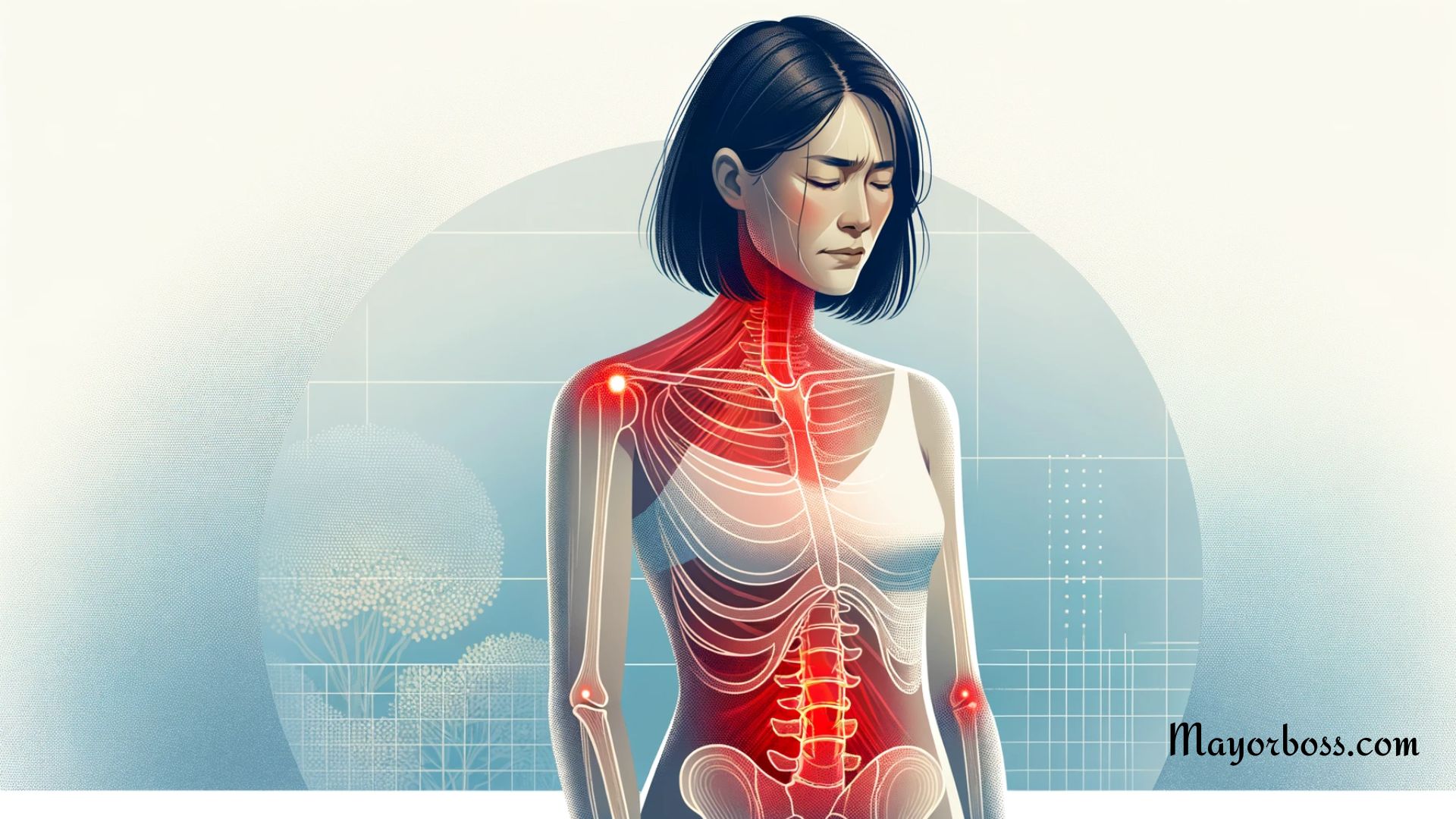
What is inflammation?
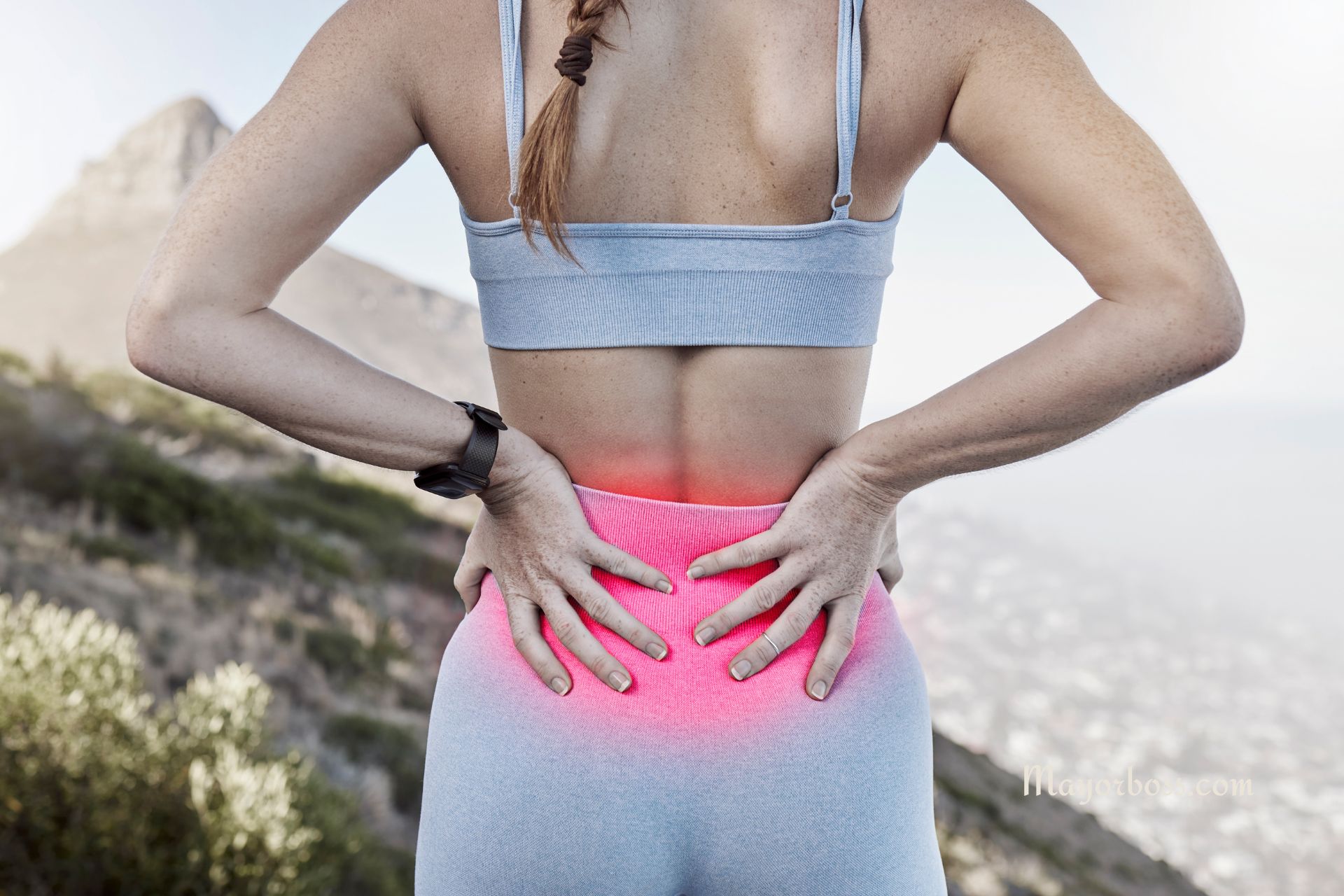
Inflammation is your body’s defense mechanism in action. It happens when your immune system recognizes damaged cells, irritants, and pathogens and begins the healing process. This can cause physical symptoms like redness, heat, swelling, and pain.
What are the signs of inflammation?
You can often tell if a part of your body is inflamed through a few key signs: redness, heat, swelling, pain, and sometimes a loss of function. For example, if you’ve ever had a sore throat, it might have been red and swollen from inflammation caused by an infection.
What causes inflammation?
Inflammation can be caused by various triggers, such as pathogens (like bacteria and viruses), physical injuries, or exposure to toxins. Sometimes, your immune system can trigger an inflammatory response when there’s no harm, which happens in autoimmune diseases. Also, occasionally, it’s a sign that your body is fighting something harmful and trying to heal itself.
Are there different types of inflammation?
Yes, there are two main types: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation usually occurs for a short while and often responds to a specific injury or infection. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is a slower and longer-term response that can last for months or even years.
How can I tell if I have chronic inflammation?
Chronic inflammation often doesn’t have the same obvious signs as acute inflammation. Instead, you might experience fatigue, fever, mouth sores, rashes, abdominal pain, or chest pain. Since these symptoms can be vague, it’s crucial to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
What diseases are linked to chronic inflammation?
Chronic inflammation can contribute to several diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and some types of cancer. It’s also associated with heart disease and diabetes. In these cases, the ongoing inflammation damages body tissues over time.
How is inflammation diagnosed?
Doctors can diagnose inflammation through a variety of methods. They might ask about your symptoms, perform a physical exam, or order tests like blood tests, which can detect high levels of certain markers of inflammation.
Can diet affect inflammation?
Absolutely. Certain foods can promote inflammation, like processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat. On the flip side, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon, and those with antioxidants, like berries, can help reduce inflammation.
Can stress cause inflammation?
Yes, chronic stress can contribute to inflammation. When you’re stressed, your body produces more of the hormone cortisol. Over time, if stress continues, cortisol can disrupt the immune system and trigger an inflammatory response.
What lifestyle changes can reduce inflammation?
To reduce inflammation, consider regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and quitting smoking. Additionally, getting enough sleep is crucial, as lack of sleep is linked to increased inflammation.
Can medications help with inflammation?
Yes, doctors often prescribe medications to help manage inflammation. These can include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, steroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for autoimmune conditions.
Are there natural remedies for inflammation?
Certainly, some natural substances are known to have anti-inflammatory effects. These include turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil. However, it’s important to talk to a doctor before starting any natural remedy, particularly if you’re already taking other medications. Also, practices like yoga and meditation can decrease stress, which in turn can reduce inflammation.
How is inflammation treated?
Treatment usually focuses on relieving pain and reducing the inflammatory response. This can include over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or aspirin, prescription medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. In certain cases, doctors may prescribe stronger anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressants.
Is inflammation always bad?
Not always. Inflammation is an essential part of the healing process. Without it, injuries wouldn’t heal, and infections could become deadly. It’s only when inflammation is excessive or lasts too long that it can become problematic.
How does chronic inflammation affect aging?
Chronic inflammation can accelerate the aging process, a concept known as “inflammaging.” It’s thought to play a role in the development of age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and cardiovascular conditions.
Can allergies cause inflammation?
Yes, allergies can trigger inflammation. When you’re allergic to something, your immune system may react to substances that typically pose no threat, leading to inflammatory responses like swelling and hives.
Can exercise reduce inflammation?
Yes, regular exercise can help reduce chronic inflammation. It can lower the levels of inflammation-promoting substances in your body and help you maintain a healthy weight, which also helps reduce inflammation.
Does inflammation affect mental health?
There’s growing evidence that chronic inflammation may play a role in mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. It’s believed that inflammatory substances can affect brain function, influencing your mood.
Can allergies cause inflammation?
Allergies are an immune response to a substance that’s usually harmless, like pollen or pet dander. This response often involves inflammation, which can cause symptoms like itching, swelling, and redness.
Is inflammation linked to autoimmune diseases?
Yes, in autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, leading to chronic inflammation. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are examples where inflammation plays a key role.
When should I see a doctor about inflammation?
If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms that you suspect might be due to inflammation, such as ongoing pain, unexplained fatigue, or persistent fevers, it’s important to schedule a visit with your doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing conditions associated with inflammation.