What Is Insulin?
What Is Insulin? Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. It allows your body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates for energy or store it for future use. Insulin helps keep your blood sugar from getting too high or too low, and imbalances can result in conditions like diabetes.
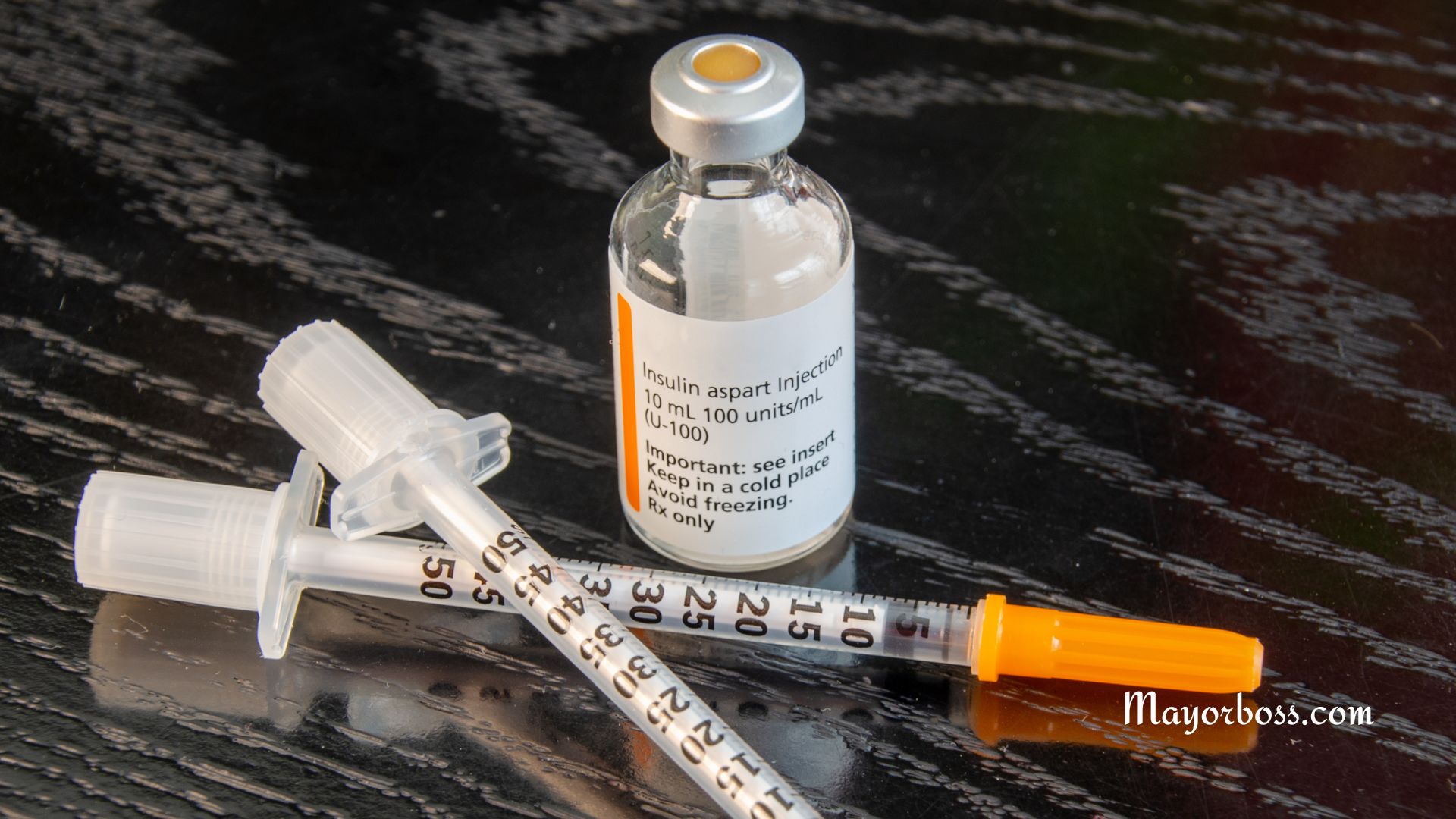
The Role of Insulin in Your Body
You eat a meal, and your body breaks down the food into various nutrients, including glucose. Your blood sugar levels rise, signaling to your pancreas that it’s time to release insulin. The insulin springs into action, helping your cells absorb the glucose and use it for energy. If there’s any glucose left over, insulin helps store it for later use. This is how insulin keeps your body humming along, ensuring you have just the right amount of energy to function.
Why Is It Important?
If you lack insulin or your body can’t use it effectively, glucose can’t enter your cells. Instead, it stays in your bloodstream, causing high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can damage your organs and tissues. On the flip side, too much insulin can lead to low blood sugar, making you feel shaky, dizzy, and even faint.
Types of Insulin
There are various types of insulin, and they differ in how quickly they work and how long their effects last.
Fast-Acting Insulin
This type starts working within 15 minutes and lasts for a few hours. It’s usually taken before meals to control spikes in blood sugar.
Long-Lasting Insulin
This type takes a while to kick in but lasts for up to 24 hours. It provides a steady level of insulin to help manage blood sugar throughout the day and night.
Pre-Mixed Insulin
This is a combination of fast-acting and long-lasting insulin. It’s often used to simplify insulin therapy for people who need multiple injections daily.
When Do You Need Insulin?
In people with Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas can’t produce insulin, so they need to take it externally. Those with Type 2 diabetes might also need insulin if other treatments aren’t effective in managing their blood sugar levels.
Side Effects and Risks
Insulin is generally safe, but like any medication, it comes with some risks. Examples of side effects include low blood sugar, weight gain, and allergic reactions.
How to Manage Insulin Levels
You can keep your insulin levels in check through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medication if necessary. Monitoring your blood sugar regularly gives you valuable information to adjust your insulin doses or make lifestyle changes.
So, whether your body produces it naturally or you needs a little help from an external source, insulin is a vital part of your body’s toolkit for managing energy and blood sugar. Keep in mind that improper management can result in health issues, so always consult with a healthcare provider for the best advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens If My Body Doesn’t Produce Enough Insulin?
If your body isn’t producing enough insulin, glucose will build up in your bloodstream instead of being absorbed by your cells. This can cause high blood sugar levels, leading to symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Over time, this condition can develop into diabetes. In severe cases, lack of insulin can result in diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Can Exercise Replace the Need for Insulin?
Exercise does help in better utilization of insulin and can improve blood sugar control. However, it can’t fully replace the need for insulin, especially in people with Type 1 diabetes, who lack the ability to produce insulin altogether. Even those with Type 2 diabetes, who might produce some insulin but not enough, often need medication or insulin therapy to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
How Is Insulin Administered?
Insulin is commonly administered through injections using a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. These devices deliver insulin just under the skin, where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. While oral insulin is under development, it’s not yet available because stomach acids break down the hormone before it can be effective.
Are There Natural Ways to Boost Insulin Sensitivity?
Yes, there are several lifestyle changes that can improve your body’s sensitivity to insulin. A balanced diet rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats can make a difference. Physical activity is another effective way to improve insulin sensitivity. Both aerobic exercises like jogging and resistance training like weightlifting have been shown to be effective.
What Are the Side Effects of Taking Insulin?
While insulin is essential for managing blood sugar, it can also have side effects. The most common one is hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, which can make you feel shaky, dizzy, and disoriented. Weight gain is another potential side effect. Allergic reactions are rare but possible and can include redness or swelling at the injection site. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing these side effects.