What is Type 1 Diabetes?
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes means your body struggles with managing blood sugar levels. This is due to a problem with insulin, a vital hormone in this process. To understand Type 1 diabetes better, it’s important to break down what’s happening in your body and how it affects you.
Understanding Insulin and Blood Sugar
Normally, your body regulates blood sugar (or glucose) levels with insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. After you eat, your blood sugar levels rise, and insulin helps to move this glucose into your cells, where it’s used for energy.
The Role of the Immune System
In Type 1 diabetes, your immune system, which usually fights off harmful bacteria or viruses, mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, your body can’t produce enough insulin.
Consequences of Low Insulin
Without enough insulin, glucose stays in your blood, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, these high levels can damage various parts of your body, such as your eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
You might notice symptoms like feeling very thirsty, urinating often, feeling very hungry even though you are eating, extreme fatigue, blurry vision, dry, itchy skin, or losing weight without trying.
Differences from Type 2 Diabetes
While Type 2 diabetes also involves blood sugar and insulin, it differs significantly. In Type 2, your body doesn’t use insulin properly and, over time, can’t make enough insulin. Type 1 is not caused by lifestyle factors like Type 2, and it usually starts in childhood or young adulthood, though it can develop at any age.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
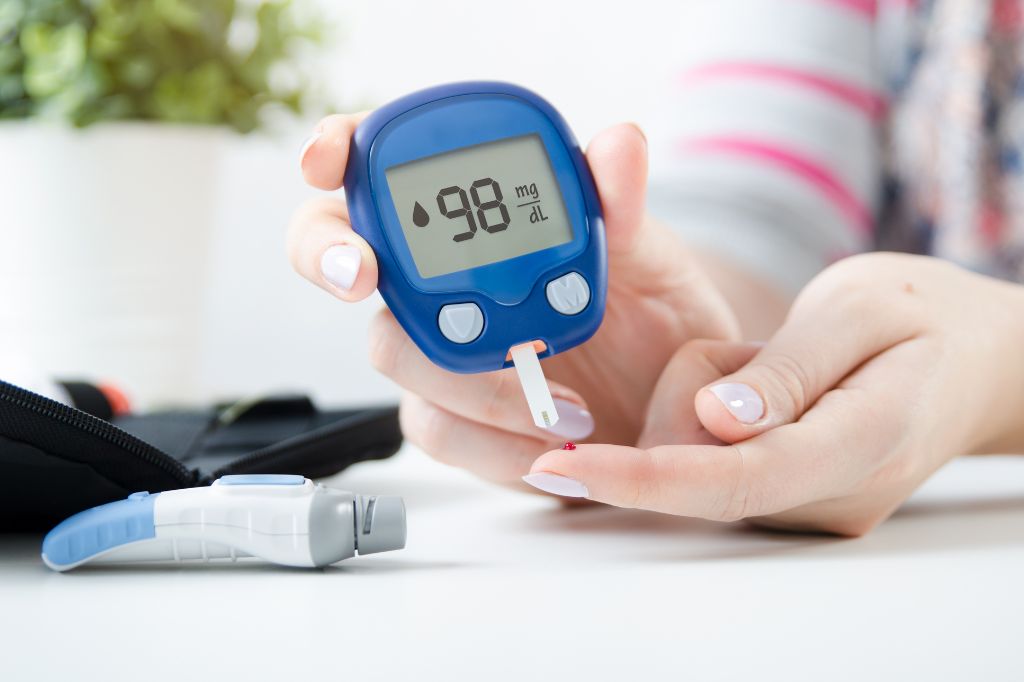
Since your body can’t make insulin, you need to take it daily to manage your blood sugar levels. This is often done through injections or an insulin pump. Monitoring your blood sugar is crucial, and you’ll need to adjust your insulin based on your blood sugar levels, what you eat, and how much you exercise.
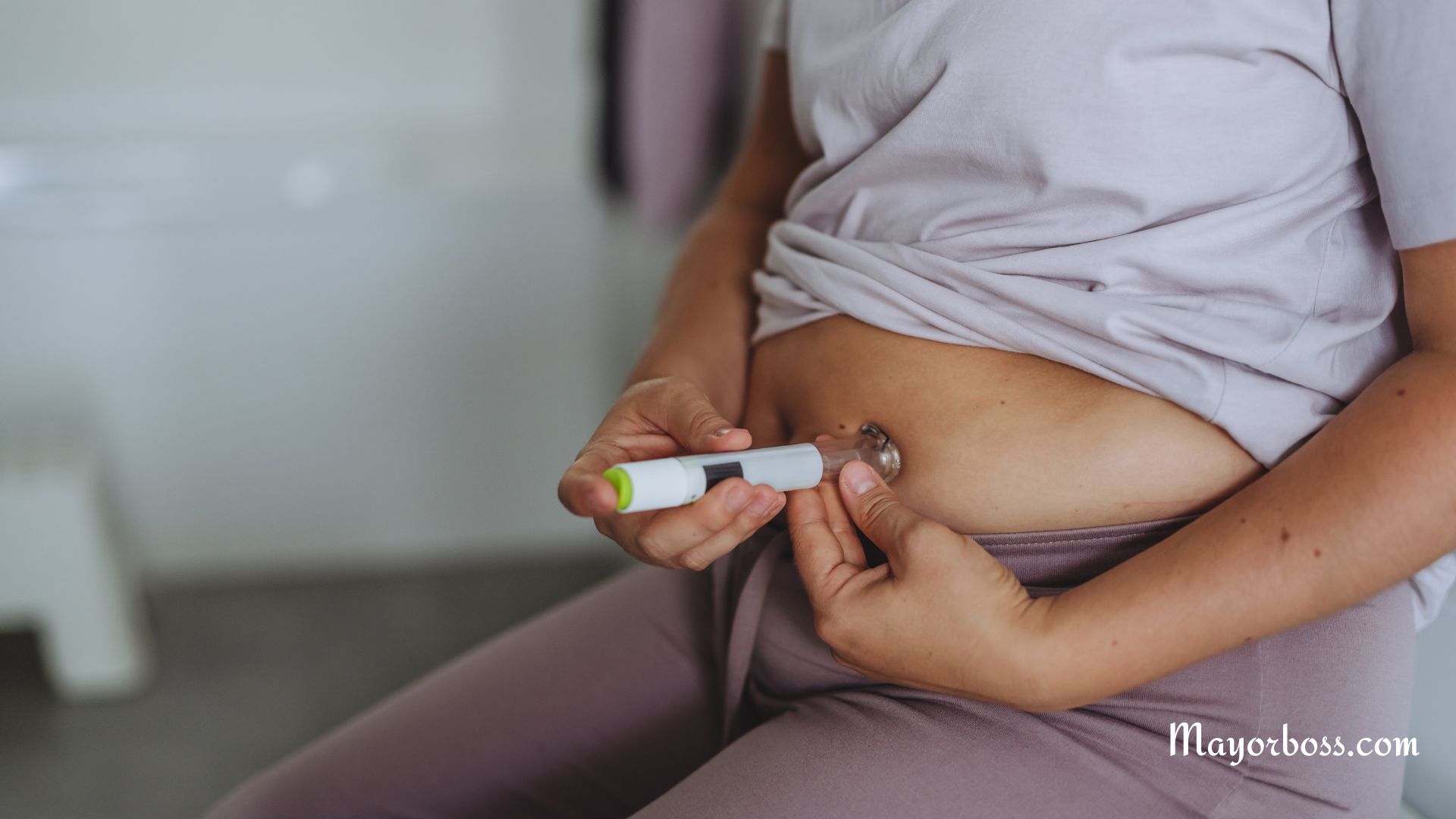

Lifestyle Considerations
While insulin is essential, other factors are also important. Eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help you manage your diabetes effectively. Moreover, regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial to monitor and manage the condition.
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong condition, but with the right management, you can lead a healthy life. The key is understanding how to balance your insulin, diet, and activity to maintain good blood sugar levels.