What Is Osteoporosis?
- Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle.
- The condition can lead to fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist.
- Osteoporosis is called the “silent disease” because there are often no symptoms until a fracture occurs.
Osteoporosis is a disease that slowly weakens bones over time, making them fragile and more likely to break. It affects millions of Americans (an estimated 44 million), yet many don’t even know they have it until they break a bone. In this post, we’ll discuss what osteoporosis is, its causes and risk factors, and how you can prevent or treat it.
What Is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease that occurs when there is too much bone loss or not enough bone formation. This makes bones weak and fragile, predisposing them to fractures. The word “osteoporosis” comes from the Greek words “osteon,” meaning bone, and “poros,” meaning holes or pores. This name refers to the deteriorated state of bone tissue in people with the disease.
Although osteoporosis can affect people of any age, gender, or race, it is most common in women over the age of 50. This is because women generally have smaller, thinner bones than men and because estrogen helps to keep bones strong. Estrogen levels decrease during menopause, which is why osteoporosis is often referred to as the “silent disease”—by the time symptoms appear, significant bone loss has already occurred.
What Are The Symptoms of Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is often called the “silent disease” because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages. As the disease progresses, bones may become weak and may break more easily.
However, some signs can indicate osteoporosis, such as:
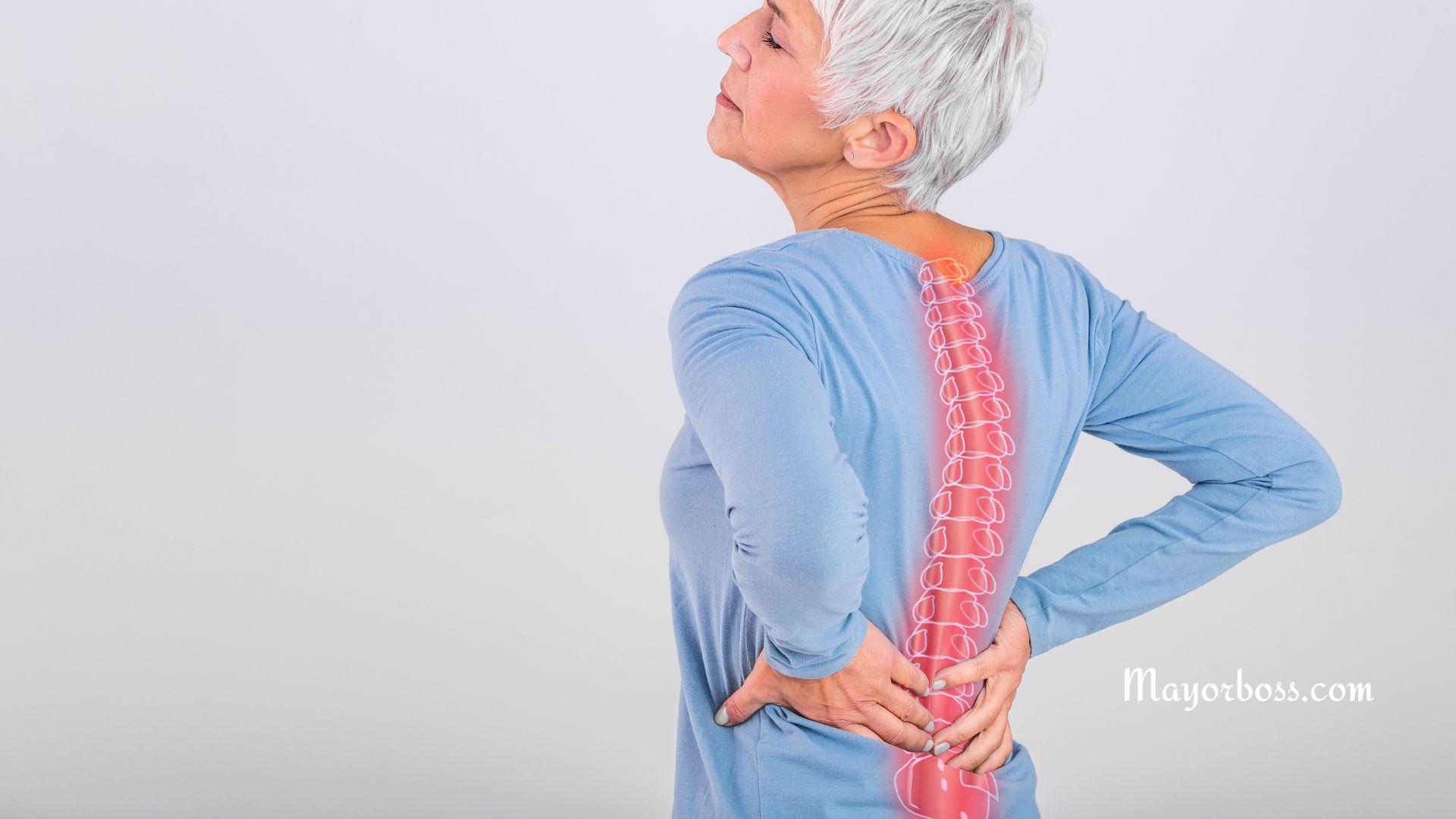
- Severe back pain
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped or hunched posture
- Weaker grip strength
- Receding gums
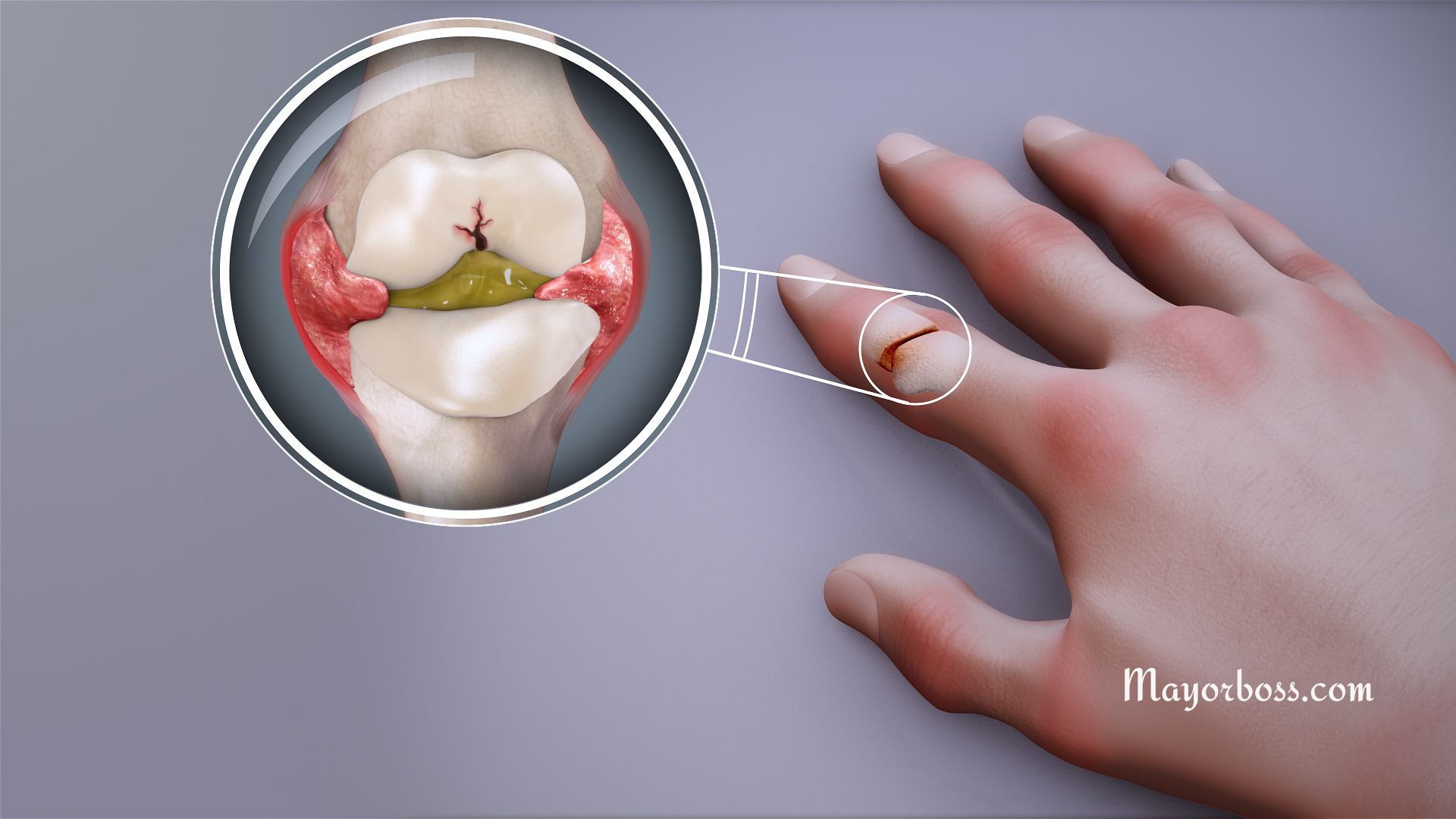
- Brittle Fingernails
- Bone fractures (osteoporosis fractures can occur in any bone, but they are most common in the hip, spine, and wrist).
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further bone loss and reduce
Osteoporosis Causes and Risk Factors
There are several risk factors for osteoporosis, including:
- family history
- gender (being female)
- age (55 or older)
- small frame size
- eating disorders or problems absorbing nutrients from food
- certain medications (steroids, anticonvulsants, cancer treatments)
- cigarette smoking
- lack of exercise
- an unhealthy diet (low in calcium and vitamin D)
- excessive alcohol consumption.
How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed?
If you think you may be at risk for developing osteoporosis—for instance, if you’re over the age of 50 or you’ve broken a bone—it’s important to talk to your doctor. They will likely order a bone density test which uses X-rays to measure how dense your bones are. The results of this test will help your doctor determine if you have osteoporosis or if you’re at risk for developing the condition.
How Is Osteoporosis Treated?
If you’ve been diagnosed with osteoporosis or if you’re at high risk for developing the condition, there are things you can do to prevent fractures and keep your bones healthy and strong!
Here are a few treatment options:
- Weight-bearing exercise: This type of exercise helps improve bone density and muscle strength. Examples include walking, jogging, stair climbing, tennis, and dancing.
- Healthy diet: Eating a nutritious diet that’s high in calcium and vitamin D can help reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis or fracture. Remember to talk to your doctor before making any dietary changes!
- Medications: If lifestyle changes aren’t enough to prevent fractures, your doctor may prescribe medication. The most common type of medication used to treat osteoporosis is bisphosphonates or denosumab, which works by slowing down bone loss and helping bones maintain their density.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a serious disease that can lead to painful fractures and mobility issues. However, it is possible to prevent or treat osteoporosis by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and working with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. If you think you may be at risk for osteoporosis—due to family history, being female, advancing age, small frame size, certain medical conditions, or medications—talk to your doctor about ways you can reduce your risk. Prevention is always the best medicine!