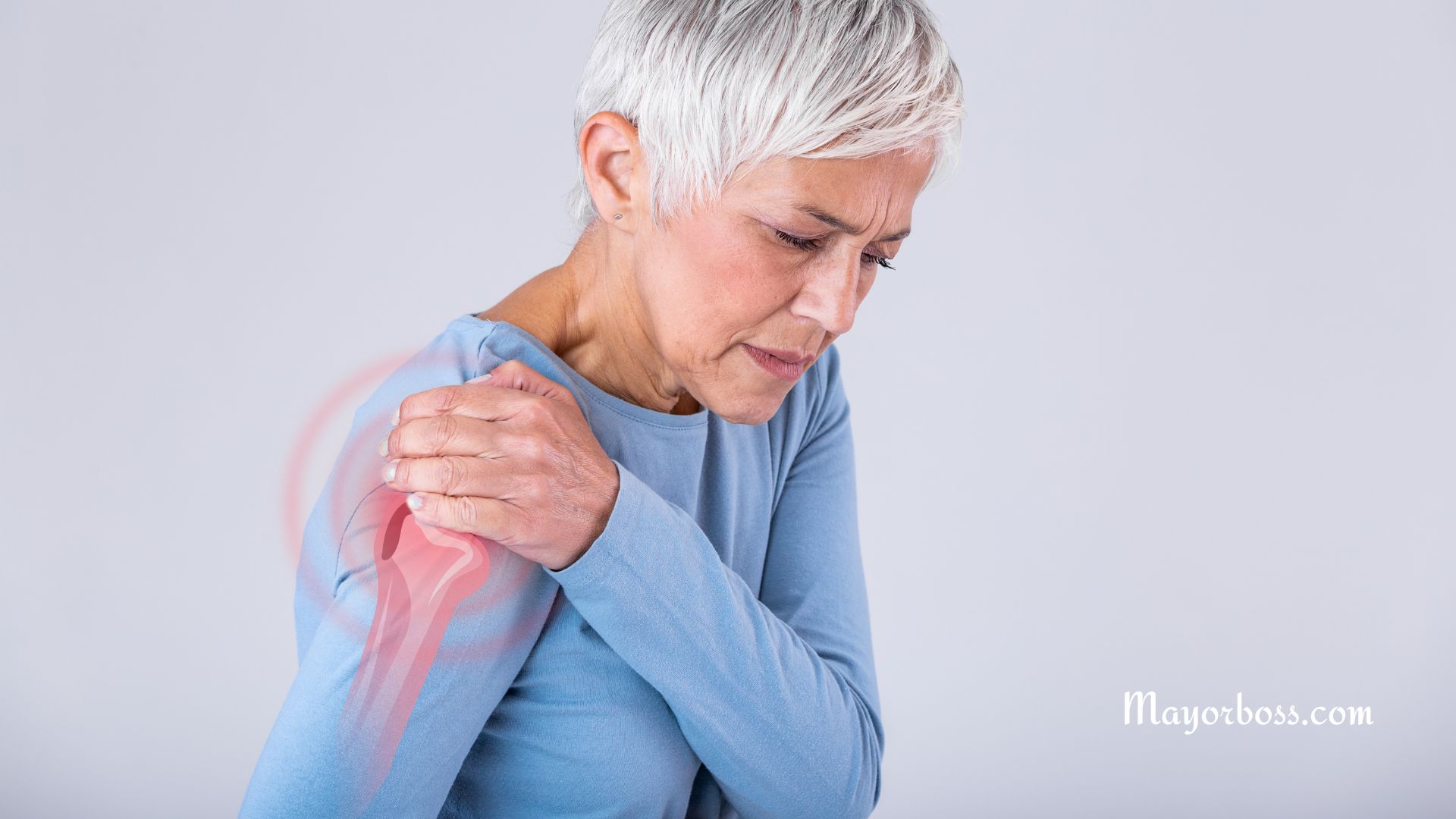
What is Bursitis?
If you have ever experienced pain in your shoulders, hips, knees, or elbows, then you may be familiar with the term “bursitis.”
Here’s what you need to know about this condition:
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa.
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissue (such as muscles, tendons, or skin). (1)
There are over 150 bursae in the human body, and they are located in joints all over the body.
When a bursa becomes inflamed, it can cause pain and stiffness in the affected joint. (2)
Bursitis is a common condition that can affect people of all ages.
It is often seen in middle-aged adults and older adults, but it can also occur in younger adults and children.
What Joints are Affected by Bursitis?
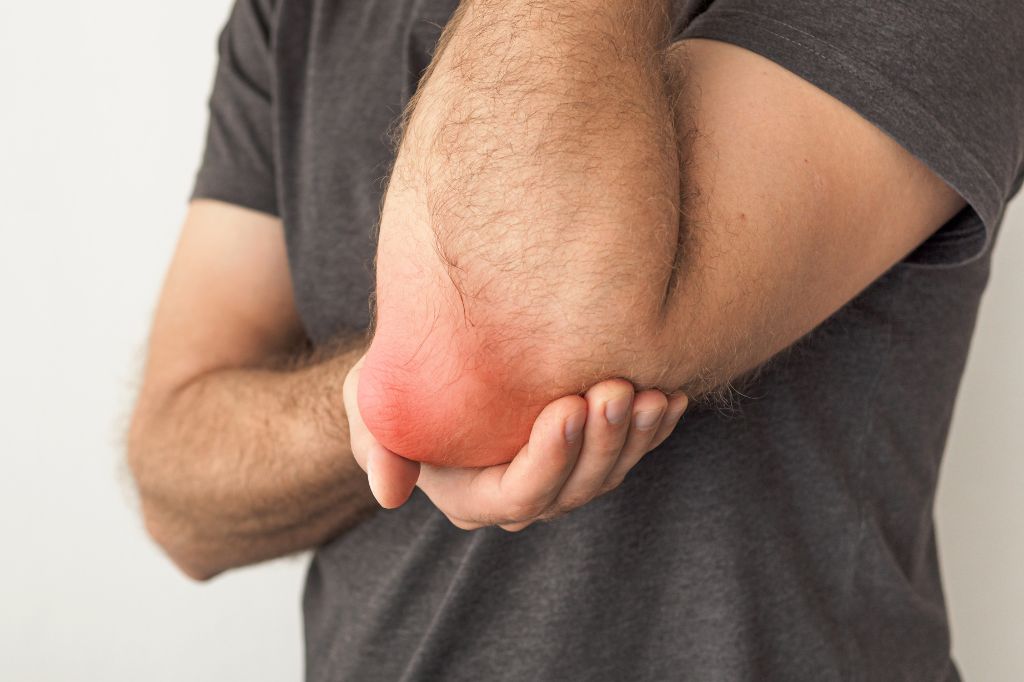
Bursitis can affect any joint in the body.
However, it is most commonly seen in the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee. (3)
- The most common form of bursitis is shoulder bursitis, also known as subacromial bursitis. This type of bursitis affects the bursa that is located under the acromion (the bony protrusion at the top of the shoulder).
- Elbow bursitis is another common type of bursitis. It can occur on the inside of the elbow (medial epicondylitis) or the outside of the elbow (lateral epicondylitis).
- Hip bursitis is another type of bursitis that can be extremely painful. It is also known as trochanteric bursitis, and it affects the bursa that is located on the outside of the hip.
- Knee bursitis is less common than other types of bursitis, but it can still occur. There are two main types of knee bursitis: prepatellar bursitis and infrapatellar bursitis. Prepatellar bursitis affects the bursa that is located in front of the kneecap, while infrapatellar bursitis affects the bursa that is located beneath the kneecap.
What Causes Bursitis?
There are a number of different things that can cause bursitis.
Some of the most common causes include:
- Repeated use of a joint: This is one of the most common causes of bursitis. When a joint is used frequently, the bursa can become inflamed. This is often seen in athletes who repetitively use the same joints during their training or in people who have jobs that require them to make a lot of repetitive motions (such as assembly line work).
- Injury: A direct injury to a joint can also cause bursitis. This can occur from a fall, a car accident, or any other type of trauma.
- Infection: An infection in the body can also lead to bursitis. The infection may be in the blood (septicemia), or it may be localized to the bursa (septic bursitis).
- Autoimmune diseases: Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can also cause bursitis. In these cases, the body’s immune system attacks the bursa, causing inflammation.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis that can also cause bursitis. In gout, uric acid crystals build up in the joints, causing inflammation.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are also at a higher risk for developing bursitis. This is because diabetes can cause changes in the body that make it more susceptible to inflammation.
- Bone Spurs: Bone spurs, or outgrowths of bone, can also rub against the bursa and cause inflammation. These are often seen in people with osteoarthritis.
What are the Symptoms of Bursitis?
The symptoms of bursitis vary depending on the location of the inflamed bursa.
However, some of the most common symptoms include:
- Pain: This is the most common symptom of bursitis. The pain can range from mild to severe, and it is often worse when the affected joint is used.
- Tenderness: The inflamed bursa can also be tender to the touch.
- Swelling: The affected area may also swell and feel warm to the touch.
- Stiffness: Bursitis can also cause stiffness in the affected joint.
- Redness: The skin around the affected area may also appear red. This is more difficult to see on darker skin.
How is Bursitis Diagnosed?
Bursitis is usually diagnosed based on a physical examination and a review of the person’s medical history.
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and how long you have been experiencing them.
They will also ask about your medical history, including any previous injuries or infections you may have had.
Your doctor will then examine the affected area.
They may use a special instrument to assess the range of motion in the joint, or they may order imaging tests, such as an MRI, to get a better look at the bursa.
How is Bursitis Treated?
The treatment for bursitis depends on the underlying cause.
If the bursitis is caused by an infection, you will need to be treated with antibiotics.
If the bursitis is caused by an autoimmune disease, you may need to be treated with immunosuppressive drugs.
For most other cases of bursitis, the treatment focuses on reducing the inflammation in the bursa.
This can be done with a variety of different methods, including:
- Rest: This is one of the most important treatments for bursitis. You need to give the inflamed bursa time to heal, and this means avoiding activities that will aggravate the condition. Your doctor may also recommend that you use crutches or a splint to keep the affected joint from moving too much.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain. Do this for 20-30 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Heat: You can also use heat to help reduce the pain and inflammation. Do this for 10-15 minutes at a time, a few times a day.
- Massage therapy: Massage is helpful for people with bursitis because it can help improve circulation and reduce inflammation.
- Compression: Wearing an elastic compression bandage can also help reduce swelling. Do not wrap it too tightly, as this can cause additional swelling.
- Elevation: Keeping the affected joint elevated above the level of your heart can also help reduce the swelling. Do this when you are resting or sleeping.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the inflamed bursa. This is usually only done if other treatments have not been successful.
What Happens if you Leave Bursitis Untreated?
Bursitis is usually a temporary condition that will go away on its own with time and rest.
However, if it is left untreated, bursitis can become chronic.
This means it will come and go, and it may last for months or even years.
Chronic bursitis can also lead to the development of other problems, such as arthritis.
If you think you may have bursitis, see your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment plan.
With proper treatment, you should be able to reduce the pain and inflammation and get back to your normal activities.
Is Walking Good for Bursitis?
Walking is a low-impact activity that can help reduce the pain and inflammation of bursitis.
However, you should avoid walking too much, as this can actually aggravate the condition.
Talk to your doctor about how much walking is safe for you.
They may also recommend other exercises, such as swimming or biking, that can help reduce the pain and inflammation without aggravating bursitis.
What Foods Should You Avoid if You Have Bursitis?
There are certain foods that can contribute to inflammation, and you should avoid these if you have bursitis.
These include:
- Sugar: Foods high in sugar, such as candy, cookies, and cake, can cause inflammation.
- Processed foods: Processed foods, such as lunch meats and frozen dinners, are also high in sugar and other additives that can cause inflammation.
- Trans fats: Trans fats, found in some margarine and processed foods, can also increase inflammation.
- Alcohol: Alcohol is a known irritant and can contribute to inflammation.
- Caffeine: Caffeine can also be an irritant and should be avoided if you have bursitis.
If you have bursitis, it is important to eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Avoiding foods that contribute to inflammation can help reduce the pain and swelling of bursitis.
Can Bursitis be Prevented?
There are some things you can do to reduce your risk of developing bursitis.
These include:
- Wearing proper footwear: Wearing shoes that fit well and support your feet can help reduce the risk of bursitis.
- Avoiding high-impact activities: Activities that put a lot of stress on your joints, such as running or playing tennis, can increase your risk of bursitis.
- Resting: If you have a joint that is injured or sore, take a break from activities that put stress on it.
- Strengthening muscles: Strong muscles help support your joints and can reduce the risk of bursitis.
- Stretching: Stretching helps keep your muscles and joints flexible and can reduce the risk of bursitis.
When Should You See a Doctor?
You should see a doctor if you are experiencing any of the symptoms of bursitis, especially if the pain is severe or persists for more than a few days.
You should also see a doctor if you have an injury or infection in the affected area.
Your doctor can help you determine the cause of your symptoms and develop a treatment plan.
Final Thoughts
Bursitis is a condition that causes inflammation of the bursa, a small sac of fluid that cushions the joints.
Bursitis is usually caused by overuse or repetitive motion, but it can also be caused by an injury or infection.
Symptoms of bursitis include pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joint.
Bursitis is usually a temporary condition that will go away on its own, but chronic cases may require medical treatment.
You can help prevent bursitis by wearing proper footwear, avoiding high-impact activities, and stretching and strengthening the muscles around your joints.
If you think you may have bursitis, see your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment plan.
With proper treatment, you should be able to reduce the pain and inflammation and get back to your normal activities.