Hyperthyroidism
Brief summary: Hyperthyroidism is a condition where your thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. This small gland in your neck controls how your body uses energy, so having too much hormone can speed things up. It’s like putting your body’s engine into overdrive. You might feel nervous or tired, lose weight, or have trouble sleeping. Sometimes it’s caused by a disease called Graves’ disease, but there are other causes too.
What Is Hyperthyroidism?
In simple terms, hyperthyroidism, also called overactive thyroid, happens when your thyroid gland is too active.
The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is like a control center for your body’s energy. When it makes too much thyroid hormone, your body’s functions speed up. This can make you feel restless and shaky or even cause your heart to beat faster.
What Causes Hyperthyroidism?
There are several things that can make your thyroid gland produce too much hormone. Some of the main ones are:
Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition that makes your thyroid gland overactive. Your immune system mistakenly attacks your thyroid, causing it to produce too much hormone.
Thyroid Nodules
Small lumps or nodules can grow on the thyroid gland. If these nodules make too much thyroid hormone, they can cause hyperthyroidism.
Too Much Iodine
According to some experts, getting too much iodine in your diet or from medications can cause your thyroid to make more thyroid hormone.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
If you have hyperthyroidism, you may notice some or all of the following:
- Feeling nervous or irritable: Your nerves might feel on edge all the time.
- Losing weight without trying: Even if you’re eating the same or more, you might still lose weight.
- Sweating more than usual: You might find yourself sweating even when it’s not hot.
- Trouble sleeping: Falling or staying asleep could become difficult.
- Heart beating fast or unevenly: Your heart might feel like it’s pounding or racing.
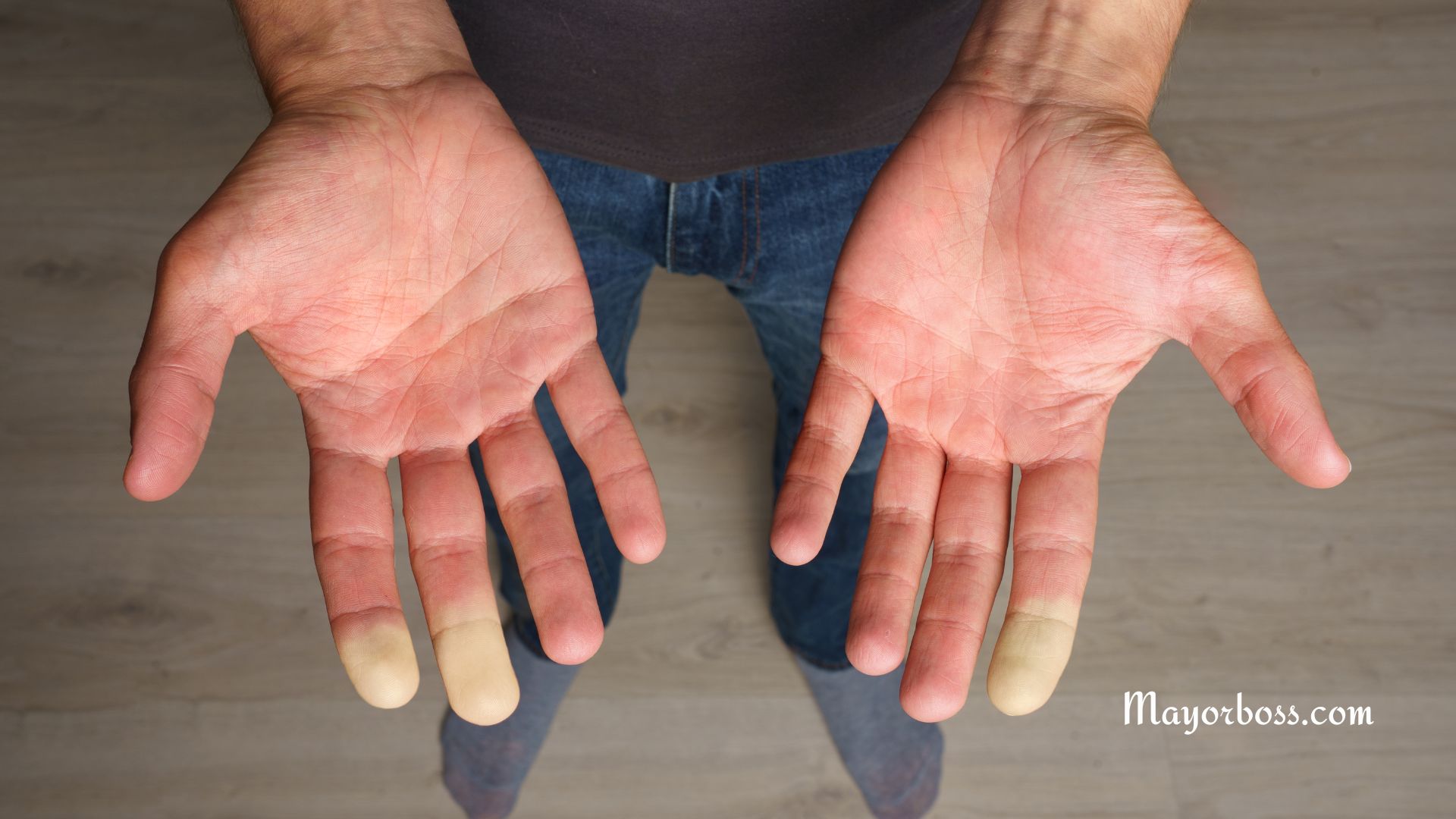
- Shaking hands or fingers: You may notice a tremor in your hands or fingers.
- Increased appetite: Even though you’re losing weight, you might feel hungrier than usual.
- Muscle weakness: Your arms or legs might feel weak or tired.
- Changes in menstrual patterns: Women might notice their periods become irregular.
- Frequent bowel movements: You might need to use the bathroom more often.
- Swelling in the neck: A swollen thyroid can cause a noticeable lump in your neck.
- Changes in your hair and skin: Your skin might become thin and fragile, and your hair might feel fine and brittle.
- Eye problems: In some cases, hyperthyroidism can cause your eyes to bulge or become irritated.
These symptoms can range from mild to severe, and not everyone will experience all of them. If you notice some of these changes in your body, it’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider. They can help you figure out what’s going on and find the right treatment for you.
How Is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
If your doctor thinks you might have hyperthyroidism, they will ask you about your symptoms and do some tests. These may include:
Blood Tests
A blood test can show if you have too much thyroid hormone in your blood.
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test
In this test, you’ll swallow a small amount of radioactive iodine. Then a special camera will take pictures of your thyroid gland to see how much iodine it’s using. This can help your doctor figure out why you have hyperthyroidism.
Treatment for Hyperthyroidism
Medications
Medications are often the go-to treatment for hyperthyroidism. Here’s how they work:
- Anti-thyroid Medications: These medicines slow down your thyroid gland’s production of hormones. They basically put the brakes on the overactive gland. Examples include methimazole and propylthiouracil.
- Beta-blockers: While not a direct treatment for hyperthyroidism, beta-blockers can help with symptoms like a rapid heart rate or tremors. They don’t affect the thyroid gland itself but can make you feel better while other treatments take effect.
Radioactive Iodine Treatment
This treatment might sound a bit scary, but it’s actually very common and safe:
- How It Works: You’ll swallow a pill or liquid with a small amount of radioactive iodine. Since your thyroid uses iodine to make hormones, it will take up the radioactive substance.
- Effect on the Thyroid: The radioactive iodine damages the cells in the thyroid that make hormones, causing the gland to shrink and produce less hormone.
- Follow-up: You’ll likely need regular check-ups after this treatment to make sure your thyroid hormone levels are where they should be.
Surgery
In some cases, you might need surgery to remove part or all of your thyroid gland. Here’s what you need to know:
- Partial Removal (Thyroid Lobectomy): If you have a smaller thyroid nodule causing hyperthyroidism, your surgeon might remove just part of the gland.
- Total Removal (Total Thyroidectomy): In more serious cases, the entire thyroid gland might be removed. This means you’ll need to take thyroid hormone replacement for the rest of your life.
- Recovery: Recovery from thyroid surgery typically requires a hospital stay and careful monitoring.
Lifestyle Changes and Supportive Care
In addition to medical treatments, your healthcare provider might suggest some changes to help you feel better:
- Eating Well: A well-balanced diet can support your overall health. Your doctor might suggest specific foods or supplements if you need them.
- Avoiding Certain Substances: You might need to avoid certain foods or medications that can affect your thyroid.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular visits to your healthcare provider will help ensure that your treatment is working and that your hormone levels are stable.
Hyperthyroidism is something that doctors know a lot about, and they can help you feel better with the right treatment. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor. They can help you figure out what’s going on and get you the right treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Hyperthyroidism Go Away on Its Own?
Generally, hyperthyroidism doesn’t go away on its own. It often requires medical treatment to control the overactive thyroid gland. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to serious health problems, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider if you suspect you have this condition.
Is Hyperthyroidism a Lifelong Condition?
Not necessarily. Some causes of hyperthyroidism, such as thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid), may be temporary. Treatment with medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery can often resolve the condition. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure that thyroid hormone levels remain stable.
Can I Still Live a Normal Life with Hyperthyroidism?
Absolutely! With the right treatment and care, most people with hyperthyroidism can lead normal, healthy lives. Managing the condition might require ongoing medical care and lifestyle adjustments, but it doesn’t have to keep you from enjoying daily activities, hobbies, and work.
Is It Safe to Get Pregnant If I Have Hyperthyroidism?
If you’re planning to become pregnant and have hyperthyroidism, it’s essential to talk to a healthcare provider. Properly managed hyperthyroidism usually doesn’t interfere with pregnancy, but uncontrolled hyperthyroidism can pose risks to both mother and baby. Your healthcare provider can help you make a treatment plan to ensure a healthy pregnancy.