Signs You Have Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a term that describes a long-lasting, low-grade form of inflammation in the body. Unlike acute inflammation, which helps you heal from injuries or infections, chronic inflammation can silently damage your organs and tissues over time.
So, how can you tell if you have chronic inflammation? According to StatPearls via the National Library of Medicine, “the common signs and symptoms of chronic inflammation are body pain, arthralgia, myalgia, chronic fatigue, insomnia, depression, anxiety, mood disorders, constipation, diarrhea, and acid reflux.”
Read on for full details.

Persistent Fatigue Can Be a Major Sign of Chronic Inflammation
One of the most common signs of chronic inflammation is persistent fatigue. If you constantly feel tired, even after a full night’s rest, chronic inflammation may be at play. When your body is fighting inflammation, it uses up more energy, which can leave you feeling drained. Fatigue due to chronic inflammation is often subtle, but it can worsen over time and interfere with daily activities.
If You Have Digestive Problems, It Could Point to Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can affect your digestive system, causing symptoms like bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation. Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are linked to chronic inflammation in the gut. If you frequently have stomach discomfort or changes in your bowel habits, this could be a sign that inflammation is affecting your digestive tract.
Joint Pain or Stiffness Can Signal Inflammatory Issues

Joint pain or stiffness is another red flag for chronic inflammation. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disease, occur when the body’s immune system wrongly attacks healthy tissues, thereby causing inflammation in the joints. This inflammation can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness, especially in the morning. If your joints often feel sore or stiff, especially without any recent injury, chronic inflammation might be the underlying cause.
Frequent Infections Could Point to Chronic Inflammation
If you’re getting sick more often than usual, such as frequent colds, respiratory infections, or sinus issues, it might be due to chronic inflammation. Inflammation can weaken your immune system over time, making it harder for your body to fight off infections. This can lead to more frequent illnesses and infections that take longer to recover from than usual.
If You Experience Brain Fog, It Could Be Linked to Inflammation
Brain fog refers to difficulties with concentration, memory, or thinking clearly, and it can be a sign of chronic inflammation. Inflammation in the brain or nervous system can interfere with your cognitive functions, leaving you feeling mentally slow or forgetful. If you often have trouble focusing or remembering things, chronic inflammation may be a factor.
Skin Issues Could Be a Visible Sign of Internal Inflammation
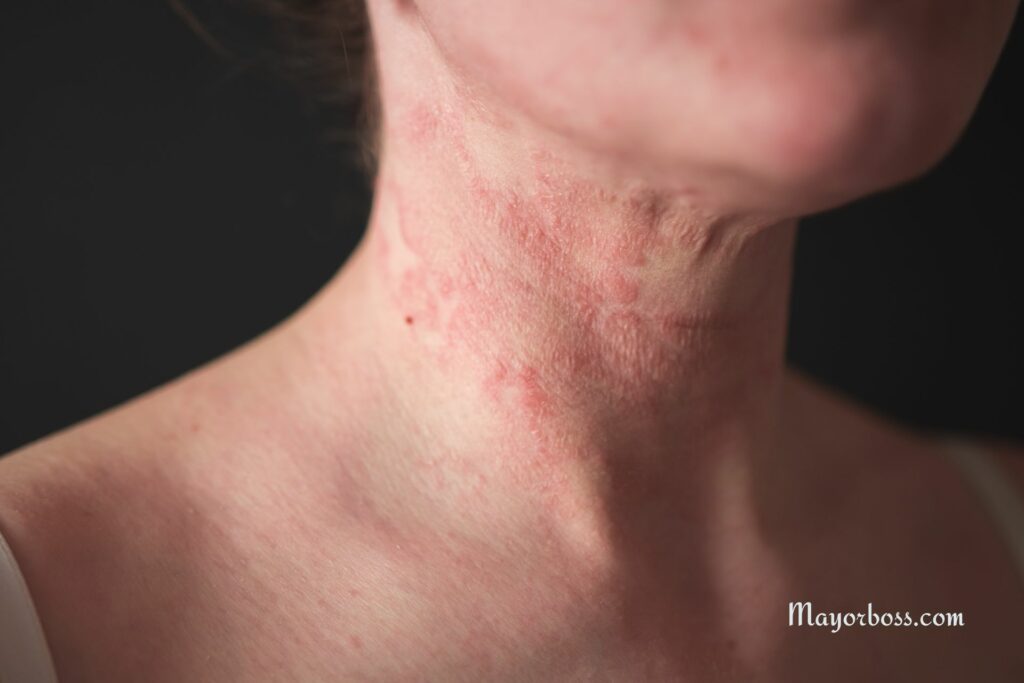
Chronic skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or acne, are often linked to chronic inflammation in the body. When inflammation affects the skin, it can lead to redness, swelling, itchiness, or even painful rashes. If you notice your skin is frequently irritated or if you develop sudden or recurring skin problems, this could be a visible sign of internal inflammation.
If You Have High Blood Pressure, It May Be Linked to Inflammation
High blood pressure (hypertension) is often associated with chronic inflammation. Inflammation can harm the lining of your blood vessels, hence causing them to narrow and leading to higher blood pressure. Over time, high blood pressure can put extra strain on your heart and increase your likelihood of heart disease. If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure or if it runs in your family, chronic inflammation might be a contributing factor.
Feeling Depressed or Anxious Could Be Related to Chronic Inflammation
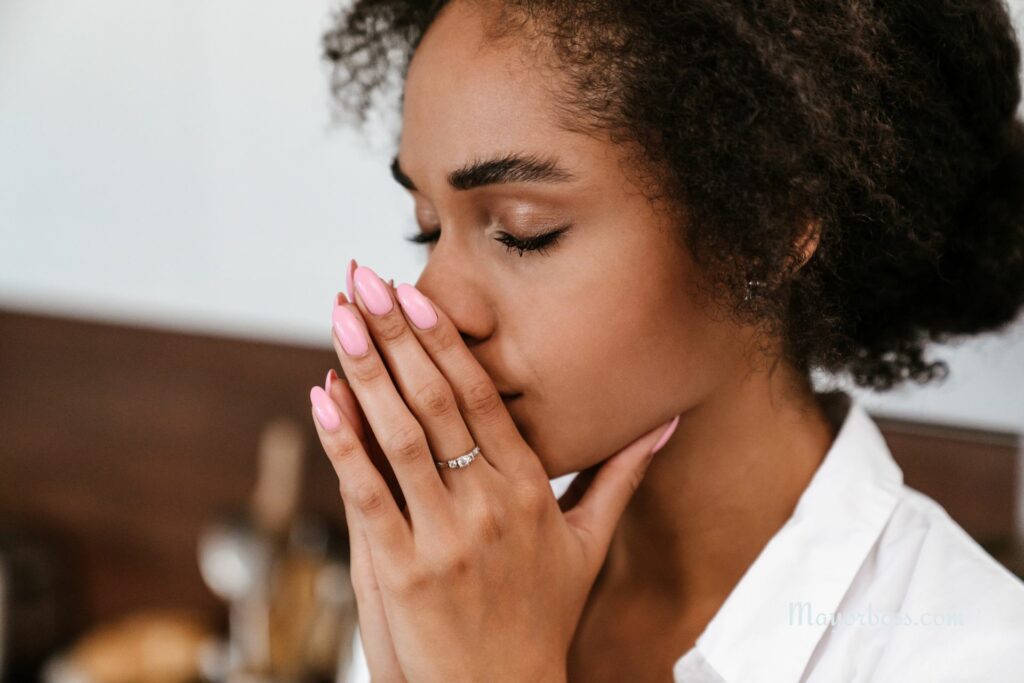

Mood disorders like depression and anxiety are increasingly being linked to chronic inflammation. Studies have found that inflammation in the brain can affect neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are involved in regulating mood. If you’ve been feeling more anxious or depressed without an obvious cause, chronic inflammation could be contributing to these emotional changes.
If You Struggle With Sleep Problems, It May Be a Sign of Inflammation
Sleep disturbances, such as trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up feeling unrefreshed, can be a sign of chronic inflammation. Inflammation can affect the hormones that regulate your sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to get restful sleep. Over time, poor sleep can worsen inflammation, creating a vicious cycle. If you’ve noticed persistent sleep problems, it might be worth considering the role inflammation plays.
Chronic Pain, Even in the Absence of Injury, Could Point to Inflammation
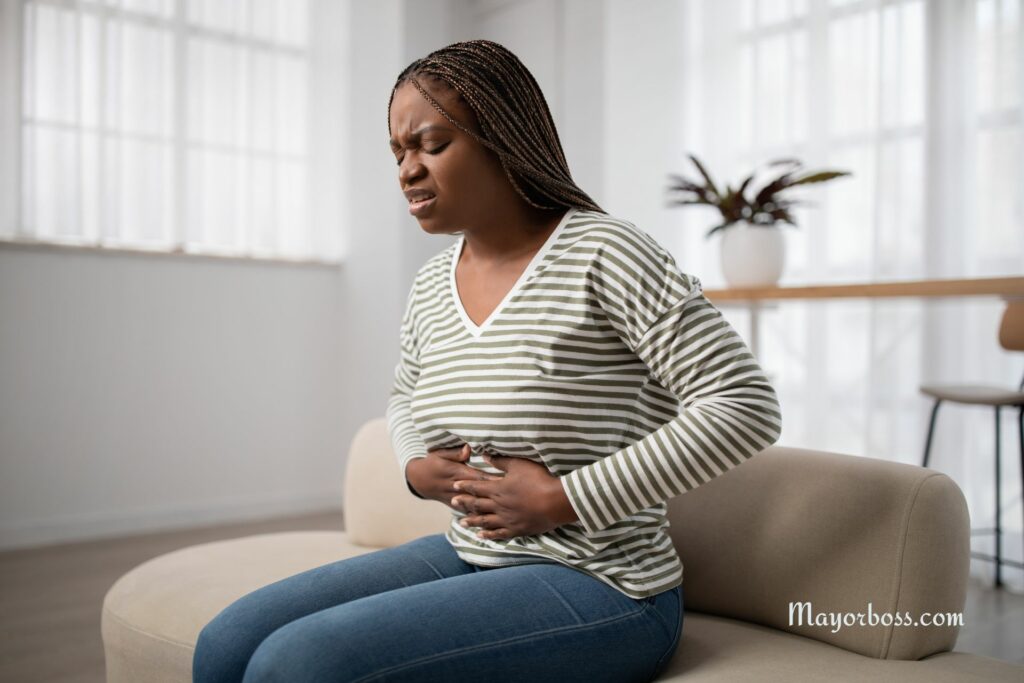

Chronic pain that doesn’t seem to have a clear cause, such as muscle aches or headaches, may be due to inflammation. This pain can persist for weeks, months, or even years and often feels like a dull, constant ache. Inflammatory conditions such as fibromyalgia are linked to chronic, widespread pain. If you have ongoing pain that can’t be explained by an injury, it might be related to inflammation.
If You Have Unexplained Weight Gain or Loss, It May Be Due to Inflammation
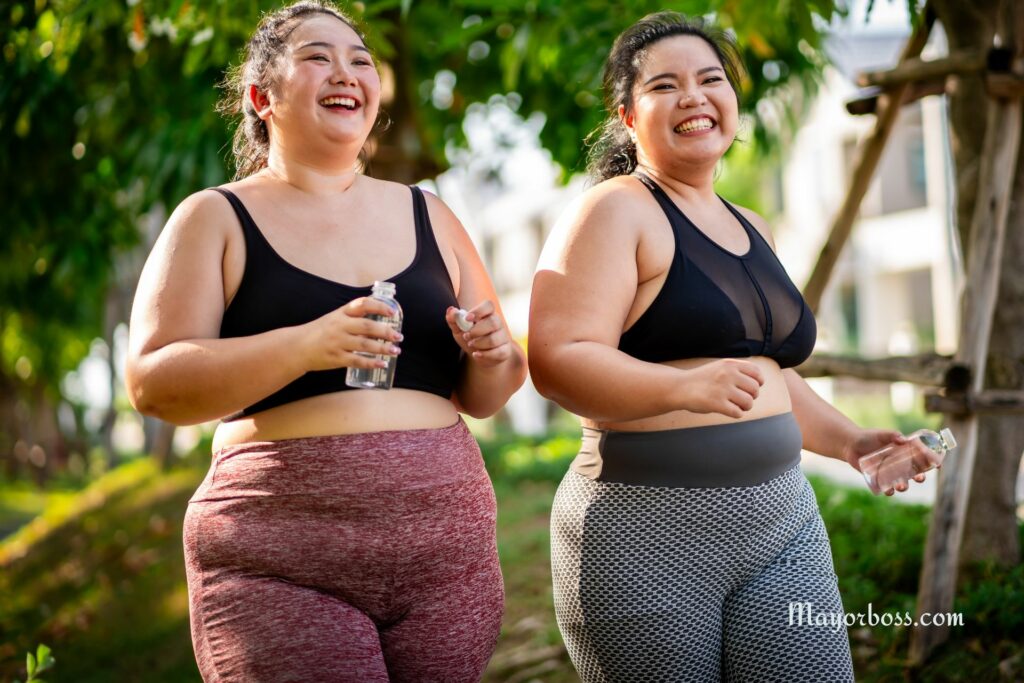

Unexplained weight changes, whether gain or loss, can also be a sign of chronic inflammation. When your body is in a state of inflammation, it can disrupt the balance of your hormones, particularly those related to metabolism and appetite. This can lead to sudden weight gain or loss without any significant changes to your diet or exercise routine. Some people may notice they’re gaining fat around their waist, which can be linked to inflammation as well.
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
Several factors can contribute to chronic inflammation. Here are some common causes:
- Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can trigger inflammation.
- Lack of exercise: Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and increase inflammation in the body.
- Chronic stress: Long-term stress can elevate levels of cortisol, a hormone that can promote inflammation.
- Exposure to toxins: Pollution, smoking, and other environmental toxins can trigger an inflammatory response.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus cause the immune system to attack healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Infections: Chronic infections, such as untreated viral or bacterial infections, can lead to prolonged inflammation.
How to Manage Chronic Inflammation
If you suspect you have chronic inflammation, here are a few ways to help manage it:
- Anti-inflammatory diet: Eating foods that fight inflammation, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fatty fish, can help reduce inflammation.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity helps lower inflammation, so try to get at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Stress management: Stress-reducing practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help control inflammation.
- Sleep hygiene: Prioritize getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help your body repair and reduce inflammation.
- Stop smoking: Smoking is a major trigger for inflammation, so quitting can help reduce your body’s inflammatory response.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase inflammation, so losing weight can help lower your risk of inflammation-related conditions.
When Should You Talk to Your Doctor?
If you think you have chronic inflammation, talk to your doctor. They may recommend blood tests, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), to check for inflammation in your body. Additionally, if you have symptoms that persist for more than a few weeks, it’s important to consult a physician. Untreated chronic inflammation can lead to more serious health problems like heart disease, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation can affect many different areas of your health, from fatigue and joint pain to digestive issues and mood changes. While the symptoms of chronic inflammation can be subtle, recognizing them early can help you take action. Making lifestyle changes, such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, can go a long way in reducing inflammation and improving your overall health. If symptoms persist, be sure to consult your doctor for a more thorough evaluation.