What is Dementia?
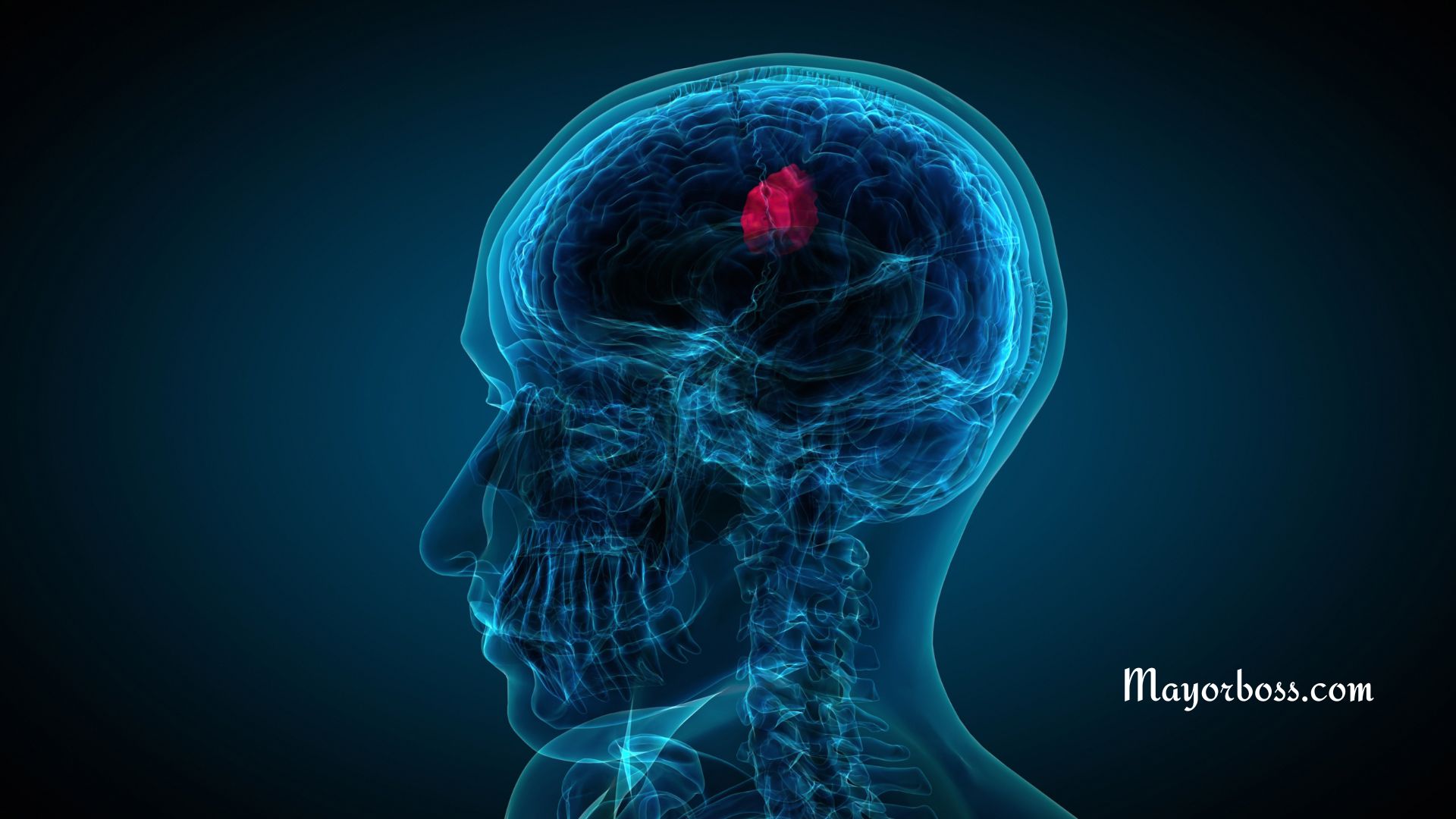
What is Dementia? Dementia isn’t a single disease. Instead, it is a broad term that describes a decline in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with doing day-to-day activities. It’s not a specific disease but rather a range of symptoms associated with issues like memory loss, impaired judgment, and difficulty with communication. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia.

What Actually Happens in Dementia?
Your brain is like a supercomputer, managing everything from memories to decision-making. Dementia throws a wrench into this system, causing problems with memory, language, problem-solving, and other cognitive skills. These disruptions make daily activities a challenge.
Cognitive Functions Affected
The key areas impacted can vary from person to person. However, some common issues include:
Memory
Forgetting things is normal, especially as you age. However, dementia takes this to another level. Imagine not being able to recall the names of your closest family members or getting lost in a place you’ve known for years. This level of memory loss is far from ordinary.
Language and Communication
You may find it increasingly difficult to find the right words in a conversation. This isn’t just about occasionally forgetting a word; it’s about consistently struggling to express yourself or understand others.
Problem-solving and Complex Tasks
Even straightforward tasks like balancing a checkbook or following a recipe can become overwhelming. The ability to think logically and solve problems takes a hit, making life more complicated.
Coordination and Motor Skills
Some people also experience a decline in their physical abilities. For example, they might struggle with tasks requiring coordination, like tying their shoes or buttoning a shirt.
Different Types of Dementia
Dementia is an umbrella term, so there are several types, each with its own set of symptoms and causes.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Accounting for about 60-80% of dementia cases, Alzheimer’s is the big player in this field. Symptoms usually start gradually and get worse over time. Memory loss is a hallmark feature, but issues with language, disorientation, and mood changes are also common.
Vascular Dementia
This type is often the result of a stroke. Unlike Alzheimer’s, the symptoms can appear suddenly. Vascular dementia affects problem-solving and speed of thought more than memory.
Lewy Body Dementia
If you notice problems with alertness and attention, it might be Lewy body dementia. This type also comes with visual hallucinations and issues with motor skills, similar to those in Parkinson’s disease.
Frontotemporal Dementia
This type affects the front and sides of the brain (the frontal and temporal lobes). Personality changes are a big clue here. You might see a shift in behavior, emotions, and even language skills.
Causes and Risk Factors
There’s no single cause of dementia; instead, it’s a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. However, age is the most significant risk factor. That said, dementia is not a normal part of aging.
Genetics
For some people, genetics play a role. If dementia runs in your family, you may be at a higher risk.
Lifestyle Choices
Examples of lifestyle factors that increase your risk include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a lack of exercise.
Medical Conditions
Certain conditions, like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, can also increase your chances of developing dementia.
Treatment and Management
There’s no cure for dementia, but medications and therapies can help manage the symptoms. For example, medications like cholinesterase inhibitors can help with memory and thinking problems in Alzheimer’s. Additionally, physical and occupational therapy may help improve daily functioning.
How Can You Prevent Dementia?
Though you can’t entirely eliminate the risk, certain steps might help you maintain better brain health.
Stay Physically Active
Engaging in regular exercise pumps more oxygen into your brain, which can keep your brain cells healthy.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and fish can help protect your brain.
Keep Your Mind Active
Activities such as puzzles, reading, or even learning a new skill can stimulate your brain, potentially delaying the onset of symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Early Signs of Dementia?
Early signs of dementia can be subtle and easily mistaken for normal aging. However, you should be alert if you notice consistent memory lapses, like forgetting appointments or misplacing items frequently. Other early symptoms include difficulty with language, such as struggling to find the right words, as well as challenges in performing familiar tasks. Additionally, mood swings, disorientation, and withdrawal from social activities could also be warning signs.
How is Dementia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing dementia involves a comprehensive medical evaluation. This often starts with a review of medical history and a physical examination. Blood tests and brain imaging studies, like MRI or CT scans, can help rule out other conditions. Neuropsychological tests may also be used to assess cognitive function. Only a healthcare provider can accurately diagnose dementia, so if you have concerns, it’s crucial to seek professional advice.
Are There Treatments for Dementia?
Although there’s no cure for dementia, treatments are available to manage symptoms. Medications such as cholinesterase inhibitors may help with cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Besides pharmaceuticals, non-drug therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy, physical exercise, and occupational therapy can also help improve daily life. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a tailored treatment plan.
Can Dementia Be Prevented?
While there’s no surefire way to prevent dementia, certain lifestyle choices can lower your risk. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, engaging in regular physical exercise, and maintaining good cardiovascular health are key preventative measures. Mental exercises like reading, solving puzzles, or learning a new skill can also keep your brain active and potentially reduce risk.
How Does Dementia Affect Daily Life?
Dementia significantly impacts daily functioning. Tasks that were once easy, such as cooking, driving, or even dressing, can become increasingly challenging. Social interactions often suffer as well, as communication becomes more difficult. As the disease progresses, more intensive care and supervision are often required. Family members may need to step in to provide support or professional caregiving services may become necessary.
Further Reading: 5 Symptoms Of Dementia To Look Out For In Loved Ones