What Is Stiff Person Syndrome? Celine Dion’s Disorder Explained
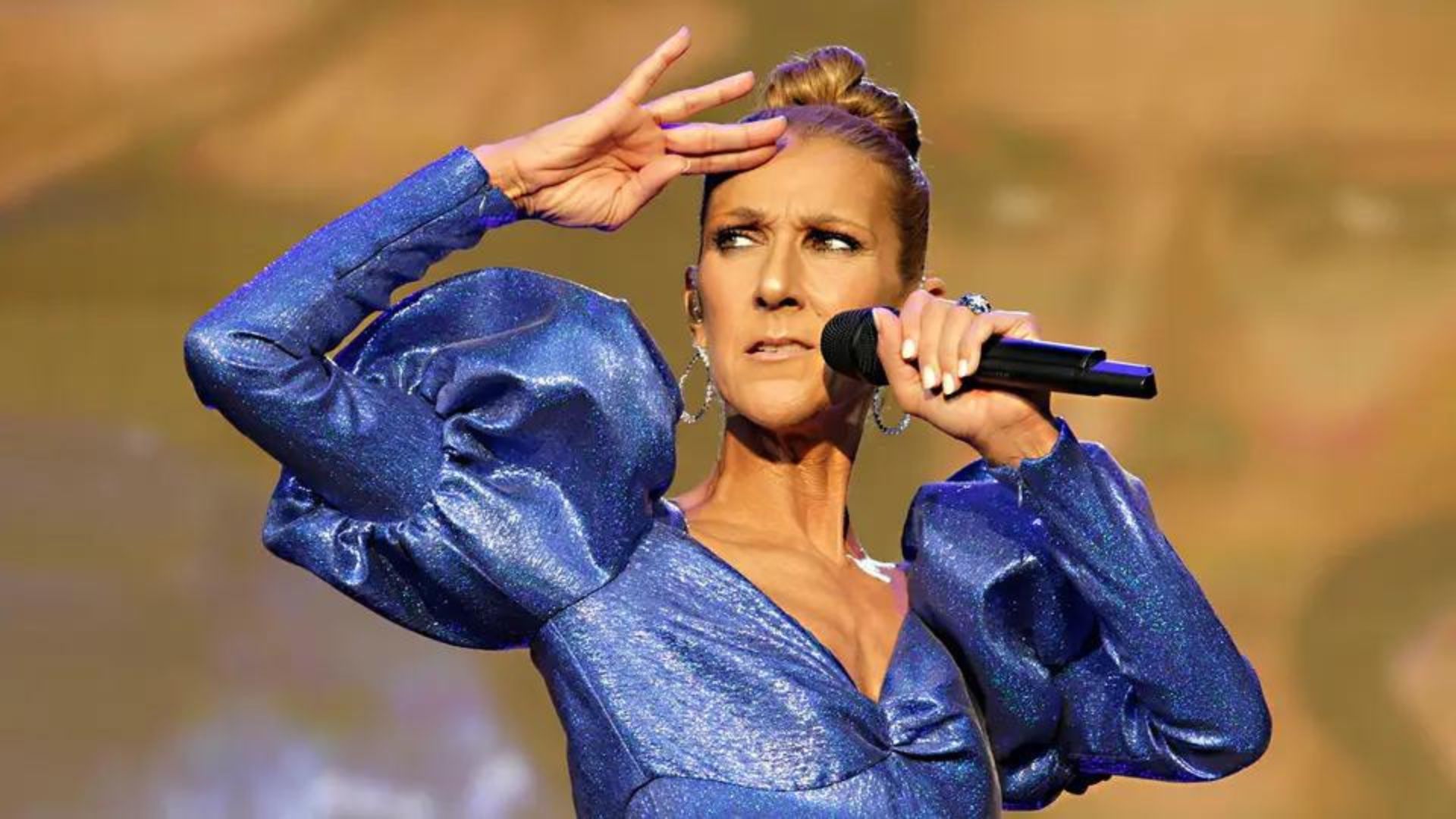
Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS) is a rare neurological condition that affects the nervous system, primarily targeting the brain and spinal cord. Known for its capacity to cause stiffness and functional impairment in muscles, SPS has recently been brought into the public spotlight due to its association with the acclaimed singer Celine Dion.
Understanding this complex disorder is crucial to demystifying the health challenges that Dion is courageously navigating.

What is Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS)?
Stiff Person Syndrome, as the name suggests, leads to stiffness and functional impairment, mainly in your trunk (torso), arms, legs, neck, and face. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) reports that over time, individuals with this condition may develop hunched-over postures. Some may even be disabled to walk or move.
In addition to stiffness, you may also experience muscle spasms, functional impairment, and heightened sensitivity to stimuli such as noise, touch, and emotional distress.
Causes and Risk Factors
The actual cause of Stiff Person Syndrome remains unclear. However, it’s believed that it’s an autoimmune disorder, meaning it happens when the body’s immune system wrongly attacks healthy tissues, in this case, the nerves. Certain antibodies found in patients with SPS are known to interfere with the function of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. This enzyme plays a pivotal role in nerve signal regulation.
While SPS can affect anyone, it’s more common in middle-aged women. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, other risk factors include having other autoimmune conditions, such as type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis, vitiligo, and pernicious anemia.
Symptoms of Stiff Person Syndrome
People with SPS might experience:
- Muscle stiffness, starting in the trunk and spreading to the limbs.
- Frequent falls due to muscle spasms and stiffness.
- Painful spasms triggered by external stimuli like sudden movements or emotional distress.
- Postural deformities such as being hunched over.
- Heightened sensitivity to touch, noise, and emotional distress.
- Emotional disturbances, like depression and anxiety.
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of Stiff Person Syndrome is usually made based on a combination of clinical symptoms and the presence of certain antibodies in the blood. Tests such as Electromyography (EMG) and lumbar puncture may also be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Once diagnosed, treatment for SPS primarily focuses on alleviating symptoms and improving functional abilities. It typically includes medications like muscle relaxants and anti-anxiety drugs to reduce stiffness and spasms. In some cases, immunotherapy may be used to moderate the body’s immune response.
Physical and occupational therapy can be beneficial in helping manage symptoms and improve mobility. Regular exercise, relaxation techniques, and a well-balanced diet also contribute to overall health and well-being.
Living with Stiff Person Syndrome
Living with Stiff Person Syndrome can be challenging due to its progressive nature and the potential for debilitating symptoms. However, with the right treatment and management plan, people with SPS can lead fulfilling lives.
The journey of celebrities like Celine Dion helps shed light on this rare condition and reminds us that a health condition does not define a person. Still, rather, their resilience and determination in the face of adversity do.